Page 203 - IJB-10-2
P. 203
International Journal of Bioprinting Optimizing inkjet bioprinting
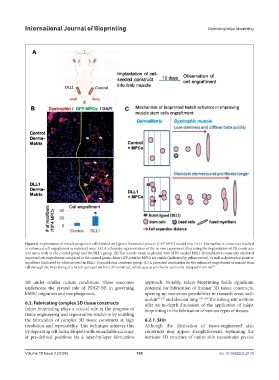
Figure 6. Implantation of muscle progenitor cells labeled with green fluorescent protein (GFP-MPC) seeded into DLL1-DermaMatrix constructs resulted
in enhanced cell engraftment in mdx/scid mice. (A) A schematic representation of the in vivo experiment illustrating the implantation of 3D constructs
into mice, both in the control group and the DLL1 group. (B) The muscle tissue implanted with MPC-seeded DLL1-DermaMatrix constructs exhibited
improved cell engraftment compared to the control group. More GFP-positive MPCs are visible (indicated by yellow arrow), as well as dystrophin-positive
myofibers (indicated by white arrows) in DLL1-DermaMatrix construct group. (C) A proposed mechanism for the enhanced engraftment of muscle stem
97
cell through the bioprinting of a Notch activator within a 3D construct, which acts as a niche for stem cells. Adapted from ref.
BB under similar culture conditions. These outcomes approach. Notably, inkjet bioprinting holds significant
underscore the pivotal role of PDGF-BB in governing potential for fabrication of thinner 3D tissue constructs,
hMSC migration and morphogenesis. opening up numerous possibilities in research areas such
as skin 99-105 and alveolar lung. 106-108 The subsequent sections
6.2. Fabricating complex 3D tissue constructs offer an in-depth discussion of the application of inkjet
Inkjet bioprinting plays a crucial role in the progress of bioprinting in the fabrication of various types of tissues.
tissue engineering and regenerative medicine by enabling
the fabrication of complex 3D tissue constructs at high 6.2.1. Skin
resolution and repeatability. This technique achieves this Although the fabrication of tissue-engineered skin
by depositing cell-laden droplets with remarkable accuracy constructs may appear straightforward, replicating the
at pre-defined positions via a layer-by-layer fabrication intricate 3D structure of native skin necessitates precise
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 195 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2135