Page 42 - IJB-10-2
P. 42
International Journal of Bioprinting DNA-functionalized hyaluronic acid bioink
specific aptamer sequence that binds to ZEN, if present, to relative concentration of polymerizing and terminator
cause a conformational change of hairpins (5) and trigger hairpins (Figure 4c and d).
28
the disintegration of the hydrogel (Figure 4b). The functionality of DNA hybrid hydrogels can be
63
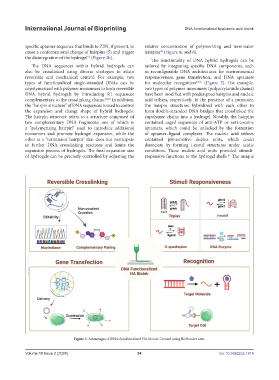
The DNA sequences within hybrid hydrogels can tailored by integrating specific DNA components, such
also be crosslinked using diverse strategies to attain as reconfigurable DNA architectures for environmental
reversible and mechanical control. For example, two responsiveness, gene transfection, and DNA aptamers
types of functionalized single-stranded DNAs can be for molecular recognition 60,66 (Figure 5). For example,
copolymerized with polymer monomers to form reversible two types of polymer monomers (polyacrylamide chains)
DNA hybrid hydrogels by introducing R1 sequences have been modified with predesigned hairpins and nucleic
complementary to the crosslinking chains. 64,65 In addition, acid tethers, respectively. In the presence of a promoter,
the “hairpin structure” of DNA sequences is used to control the hairpin structures hybridized with each other to
the expansion and change shape of hybrid hydrogels. form double-stranded DNA bridges that crosslinked the
The hairpin structure refers to a structure composed of copolymer chains into a hydrogel. Notably, the hairpins
two complementary DNA fragments; one of which is contained caged sequences of anti-ATP or anti-cocaine
a “polymerizing hairpin” used to introduce additional aptamers, which could be unlocked by the formation
monomers and promote hydrogel expansion, while the of aptamer–ligand complexes. The nucleic acid tethers
other is a “terminator hairpin” that does not participate contained pH-sensitive duplex units, which could
in further DNA crosslinking reactions and limits the dissociate by forming i-motif structures under acidic
expansion process of hydrogels. The final expansion size conditions. These nucleic acid units provided stimuli-
of hydrogels can be precisely controlled by adjusting the responsive functions to the hydrogel shells. The unique
67
Figure 5. Advantages of DNA-functionalized HA bioink. Created using BioRender.com.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 34 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1814