Page 46 - IJB-10-2
P. 46
International Journal of Bioprinting DNA-functionalized hyaluronic acid bioink
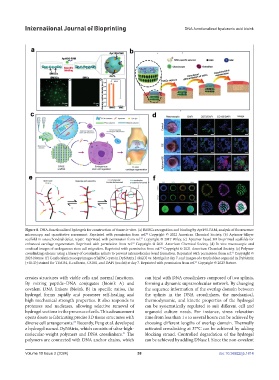
Figure 8. DNA-functionalized hydrogels for construction of tissue in vitro. (a) BMSCs recognition and binding by Apt19S-FAM, analysis of fluorescence
microscopy, and quantitative assessment. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright © 2022 American Chemical Society. (b) Aptamer-bilayer
80
scaffold in osteochondral defect repair. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright © 2017 Wiley. (c) Aptamer-based 3D-bioprinted scaffolds for
81
enhanced cartilage regeneration. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright © 2021 American Chemical Society. (d) In vivo macroscopic and
82
confocal images of endogenous stem cell migration. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright © 2021 American Chemical Society. (e) Polymer
82
crosslinking scheme using a library of crosslinker splints to prevent intramolecular bond formation. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright ©
41
2023 Nature. (f) Confocal microscopy images of hiPSC cysts in DyNAtrix [+RGD] vs. Matrigel at day 7, and images of a trophoblast organoid in DyNAtrix
[+RGD] stained for TEAD4, E-cadherin, GCM1, and DAPI (nuclei) at day 7. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright © 2023 Nature.
41
creates structures with viable cells and normal functions. can bind with DNA crosslinkers composed of two splints,
By mixing peptide–DNA conjugates (bioink A) and forming a dynamic supramolecular network. By changing
covalent DNA linkers (bioink B) in specific ratios, the the sequence information of the overlap domain between
hydrogel forms rapidly and possesses self-healing and the splints in the DNA crosslinkers, the mechanical,
high mechanical strength properties. It also responds to thermodynamic, and kinetic properties of the hydrogel
proteases and nucleases, allowing selective removal of can be systematically regulated to suit different cell and
hydrogel sections in the presence of cells. This advancement organoid culture needs. For instance, stress relaxation
opens doors to fabricating precise 3D tissue structures with time from less than 1 s to several hours can be achieved by
diverse cell arrangements. Recently, Peng et al. developed choosing different lengths of overlap domain. Thermally
84
a hydrogel named DyNAtrix, which consists of ultra-high- activated crosslinking at 37°C can be achieved by adding
41
molecular-weight polymers and DNA crosslinkers. The blocking strand. Controlled degradation of the hydrogel
polymers are connected with DNA anchor chains, which can be achieved by adding DNase I. Since the non-covalent
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 38 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1814