Page 43 - IJB-10-2
P. 43
International Journal of Bioprinting DNA-functionalized hyaluronic acid bioink
sequences and structures of these DNA elements can 4. Implications of advanced bioinks for car-
encode functional details, imbuing hydrogels with precise tilage engineering
and tailored recognition and response to external stimuli.
This inherent programmability of DNA affords researchers Utilizing customizable structural configurations, DNA-
the flexibility to adeptly design and regulate smart functionalized hydrogels exhibit the ability to regulate
hydrogel. DNA-functionalized HA hydrogels combine cellular behavior and fate, providing essential physical,
68
the advantages of both HA and DNA as biomaterials for chemical, and biological cues necessary for cellular
cartilage engineering. HA provides biocompatibility, proliferation. 69,70 These functionalized hydrogels have
biodegradability, and low immunogenicity, as well broad application prospects in cartilage regeneration
as mimics the natural component of cartilage ECM. and can be classified, according to their modes of action,
DNA provides structural programmability, stimuli into different categories, such as cell protection, drug
responsiveness, molecular recognition, and gene delivery delivery, cell recruitment, gene transfection, and reversible
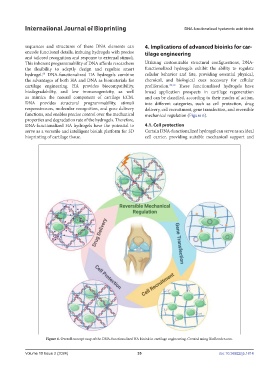
functions, and enables precise control over the mechanical mechanical regulation (Figure 6).
properties and degradation rate of the hydrogels. Therefore,
DNA-functionalized HA hydrogels have the potential to 4.1. Cell protection
serve as a versatile and intelligent bioink platform for 3D Certain DNA-functionalized hydrogel can serve as an ideal
bioprinting of cartilage tissue. cell carrier, providing suitable mechanical support and
Figure 6. Overall concept map of the DNA-functionalized HA bioink in cartilage engineering. Created using BioRender.com.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 35 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1814