Page 41 - IJB-10-2
P. 41
International Journal of Bioprinting DNA-functionalized hyaluronic acid bioink
These units are connected by β-(1,3) and β-(1,4) glycosidic molecular chain. For example, HA reacts with maleic
bonds. HA encompasses both polar segments with positive anhydride to form HA-Mal, which then forms a thioether
and negative charges, as well as non-polar portions lacking bond with thiol groups in deprotected thiolated oligo-
charge separation, which contribute to the formation of DNA. After mixing HA modified with two complementary
intermolecular linkages. The fundamental structure of single-stranded DNAs, the hybridized complementary
HA consists of a continuous polymer chain covalently strands serve as crosslinking points to form a hydrogel 62
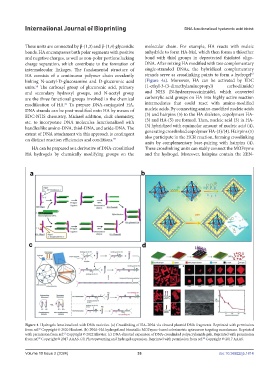
linking N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and D-glucuronic acid (Figure 4a). Moreover, HA can be activated by EDC
58
units. The carboxyl group of glucuronic acid, primary (1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide)
and secondary hydroxyl groups, and N-acetyl group and NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide), which converted
are the three functional groups involved in the chemical carboxylic acid groups on HA into highly active reaction
modification of HA. To prepare DNA-conjugated HA, intermediates that could react with amino-modified
61
DNA strands can be post-modified onto HA by means of nucleic acids. By connecting amino-modified nucleic acids
EDC-NHS chemistry, Michael addition, click chemistry, (3) and hairpins (5) to the HA skeleton, copolymers HA-
etc. to incorporate DNA molecules functionalized with (3) and HA-(5) are formed. Then, nucleic acid (3) in HA-
handles like amino-DNA, thiol-DNA, and azide-DNA. The (3) hybridized with equimolar amount of nucleic acid (4),
extent of DNA attachment via this approach is contingent generating crosslinked copolymer HA-(3)/(4). Hairpins (5)
also participate in the HCR reaction, forming crosslinking
on distinct reaction efficiencies and conditions.
59
units by complementary base-pairing with hairpins (4).
HA can be prepared as a derivative of DNA-crosslinked These crosslinking units can stably connect the MOFzyme
HA hydrogels by chemically modifying groups on the and the hydrogel. Moreover, hairpins contain the ZEN-
Figure 4. Hydrogels functionalized with DNA moieties. (a) Crosslinking of HA–DNA via cleaved plasmid DNA fragments. Reprinted with permission
from ref. Copyright © 2020 Hindawi. (b) DNA–HA hydrogel and bimetallic MOFzyme-based colorimetric aptasensor targeting zearalenone. Reprinted
62
with permission from ref. Copyright © 2022 Elsevier. (c) DNA-directed expansion of DNA-crosslinked polyacrylamide gels. Reprinted with permission
63
from ref. Copyright © 2017 AAAS. (d) Photopatterning and hydrogel expansion. Reprinted with permission from ref. Copyright © 2017 AAAS.
28
28
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 33 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1814