Page 448 - IJB-10-2
P. 448
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed silicon nitride-PEEK implants
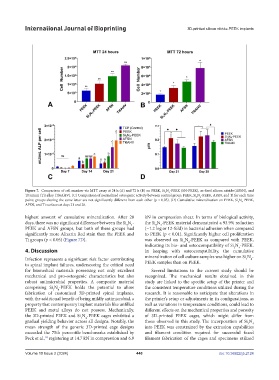
Figure 7. Comparison of cell number via MTT assay at 24 h (A) and 72 h (B) on PEEK, Si N -PEEK (SN-PEEK), as-fired silicon nitride (AFSN), and
4
3
Titanium (Ti) alloy (Ti6Al4V). (C) Comparison of normalized osteogenic activity between control group, PEEK, Si N -PEEK, AFSN, and Ti for each time
3
4
point; groups sharing the same letter are not significantly different from each other (p < 0.05). (D) Cumulative mineralization on PEEK, Si N -PEEK,
4
3
AFSN, and Ti surfaces at days 21 and 28.
highest amount of cumulative mineralization. After 28 kN in compression shear. In terms of biological activity,
days, there was no significant difference between the Si N - the Si N -PEEK material demonstrated a 93.9% reduction
4
3
4
3
PEEK and AFSN groups, but both of these groups had (~1.2 log or 12-fold) in bacterial adhesion when compared
significantly more Alizarin Red stain than the PEEK and to PEEK (p < 0.01). Significantly higher cell proliferation
Ti groups (p < 0.05) (Figure 7D). was observed on Si N -PEEK as compared with PEEK,
4
3
indicating its bio- and osteocompatibility of Si N -PEEK.
3
4
4. Discussion In keeping with osteocompatibility, the cumulative
Infection represents a significant risk factor contributing mineralization of cell culture samples was higher on Si N -
3
4
to spinal implant failures, underscoring the critical need PEEK samples than on PEEK.
for biomedical materials possessing not only excellent Several limitations to the current study should be
mechanical and pro-osteogenic characteristics but also recognized. The mechanical results obtained in this
robust antimicrobial properties. A composite material study are linked to the specific setup of the printer and
comprising Si N -PEEK holds the potential to allow the consistent temperature conditions utilized during the
4
3
fabrication of customized 3D-printed spinal implants, research. It is reasonable to anticipate that alterations in
with the additional benefit of being mildly antimicrobial, a the printer’s setup or adjustments in its configurations, as
property that contemporary implant materials like unfilled well as variations in temperature conditions, could lead to
PEEK and metal alloys do not possess. Mechanically, different effects on the mechanical properties and porosity
the 3D-printed PEEK and Si N -PEEK cages exhibited a of 3D-printed PEEK cages, which might differ from
3
4
gradual yielding behavior across all designs. Notably, the those observed in this study. The incorporation of Si N
3
4
mean strength of the generic 3D-printed cage designs into PEEK was constrained by the extrusion capabilities
exceeded the 75th percentile benchmarks established by and filament condition required for successful fused
Peck et al., registering at 14.7 kN in compression and 6.9 filament fabrication of the cages and specimens utilized
28
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 440 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2124