Page 214 - IJB-10-3
P. 214
International Journal of Bioprinting Sr on GO enhances PLLA/PGA scaffold
of the LG scaffold. As shown in Figure 5a–f, the surface and subsequently attract PO to form the apatite layer
3-
4
of the scaffolds showed small holes due to degradation. deposition. At the same time, Sr element was also detected
70
There were a number of particles on the surface of the in the apatite layer deposition on the surface of the LG/
LG/GP and LG/GPSr1.5 scaffolds, which might be the GPSr1.5 scaffold, indicating that Sr partially replaced Ca
apatite layer deposition generated during immersion in in the apatite layer. The above results showed that the LG/
71
SBF. The elemental composition of the scaffolds after SBF GPSr1.5 scaffold had good bioactivity.
immersion was analyzed by EDS, as shown in Figure 5g–
i. It was found that the deposition on the surface of the A scaffold should have good cytocompatibility,
LG/GP and LG/GPSr1.5 scaffolds was mainly composed an attribute important for promoting cell growth and
of Ca and P elements. This indicated that calcium and proliferation without triggering an immune response. The
phosphorus crystals grew on the surface of the LG/GP and cytocompatibility of the LG/GPSr1.5 scaffold was tested
LG/GPSr1.5 scaffolds after immersion in SBF, because of and compared with that of the LG scaffold. BMSCs were
the presence of PDA in scaffold, which was considered inoculated on the two kinds of scaffolds, and morphology
to be an effective promoting factor for apatite deposition of the cells cultured for 1, 3, and 5 days was visualized using
under physiological conditions. 68,69 The phenolic hydroxyl SEM. The cells had good adhesion and extension on the
groups in PDA could sequester Ca from SBF solution surface of both LG and LG/GPSr1.5 scaffolds, as shown
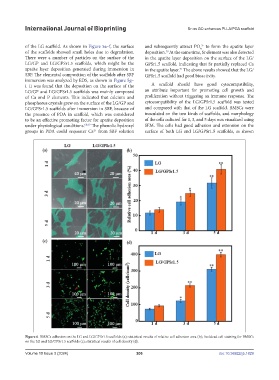
2+
Figure 6. BMSCs adhesion on the LG and LG/GPSr1.5 scaffolds (a); statistical results of relative cell adhesion area (b); live/dead cell staining for BMSCs
on the LG and LG/GPSr1.5 scaffolds (c); statistical results of cell density (d).
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 206 doi: 10.36922/ijb.1829