Page 588 - IJB-10-3
P. 588
International Journal of Bioprinting 4D printing & simulation for biomedicine
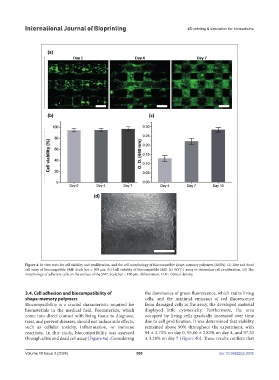
Figure 4. In vitro tests for cell viability and proliferation, and the cell morphology of biocompatible shape-memory polymers (SMPs). (a) Live and dead
cell assay of biocompatible SMP. Scale bar = 500 μm. (b) Cell viability of biocompatible SMP. (c) WST-1 assay to determine cell proliferation. (d) The
morphology of adherent cells on the surface of the SMP. Scale bar = 100 μm. Abbreviation: O.D.: Optical density.
3.4. Cell adhesion and biocompatibility of the dominance of green fluorescence, which stains living
shape-memory polymers cells, and the minimal emission of red fluorescence
Biocompatibility is a crucial characteristic required for from damaged cells in the assay, the developed material
biomaterials in the medical field. Biomaterials, which displayed little cytotoxicity. Furthermore, the area
come into direct contact with living tissue to diagnose, occupied by living cells gradually increased over time
treat, and prevent diseases, should not induce side effects, due to cell proliferation. It was determined that viability
such as cellular toxicity, inflammation, or immune remained above 90% throughout the experiment, with
reactions. In this study, biocompatibility was assessed 94 ± 2.73% on day 0, 95.00 ± 2.82% on day 4, and 97.20
through a live and dead cell assay (Figure 4a). Considering ± 3.28% on day 7 (Figure 4b). These results confirm that
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 580 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3035