Page 38 - IJB-4-1
P. 38
Jang T-S, et al.
built by the machine prints on the glass plate, and placed printing method in which thermoplastic filaments such
in between the light source and the fabrication platform. as poly(lactice acid) (PLA) and acrylonitrile-butadiene-
The fabrication principle of this technique resembles the styrene (ABS) are melted by heating and extruded on the
previous SL printers, but it has unique features of process build plate [35] . However, all techniques with a melting
and support material design. Every fresh photocurable process are not suitable processes to deposit hydrogel
materials are coated on top of fabricated structure by since applying heat to hydrogel can cause a decrease
spraying method. After UV light irradiation on the liquid in biocompatibility and thermal degradation [3,36] . Heat
materials, uncured material is removed by vacuum and treatment for sol-gel transition of hydrogels at elevated
filled with a wax as a supporter for the next layer (Figure temperatures induces critical damage to cells loaded in
[37]
1D). During these repeating this process, planarization the hydrogels, resulting in acute cell death . In addition,
or levelling procedure of coated new layer is necessary unlike thermoplastic polymers, hydrogels are in the form
for the accurate and reliable finishing. After printing, the of viscous liquid and cannot be used as materials for
wax is melted away from the 3D structure [18,29] . FDM as they cannot be shaped into filament due to their
2.2 Nozzle-based Hydrogel 3D Printing Systems poor mechanical properties.
Therefore, most of hydrogel-based 3D printings studies
Nozzle-based printing method is the most popular are performed by printing techniques without melting
technique to build hydrogel based scaffolds. The melted process including five major categories, 3D bioplotting,
polymers or viscous liquids are forced and extruded pressure-assisted microsyringe (PAM), direct ink writing
out of a nozzle, syringe or orifice and solidified onto a (DIW), low-temperature deposition modelling (LDM),
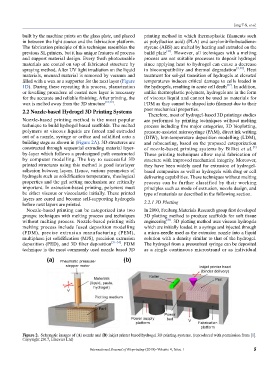
building stage as shown in (Figure 2A). 3D structures are and robocasting, based on the proposed categorization
constructed through sequential extruding material layer- of nozzle-based printing systems by Billiet et al.
[3]
by-layer which follows a predesigned path constructed These printing techniques allow rapid fabrication of
by computer modelling. The key to successful 3D structure with improved mechanical integrity. Moreover,
printed structures using this method is good interlayer they have been widely used for extrusion of hydrogel-
adhesion between layers. Hence, various parameters of based composites as well as hydrogels with drug or cell
hydrogels such as solidification temperature, rheological delivering capabilities. These techniques without melting
properties and the gel setting mechanism are critically process can be further classified by their working
important. In extrusion-based printing, polymers must principles such as mode of extrusion, nozzle design, and
be either viscous or viscoelastic initially. These printed type of materials as described in the following section.
layers are cured and become self-supporting hydrogels
before next layers are printed. 2.2.1 3D Plotting
Nozzle-based printing can be categorized into two In 2000, Freiburg Materials Research group first developed
groups: techniques with melting process and techniques 3D plotting method to produce scaffolds for soft tissue
without melting process. Nozzle-based printing with engineering . 3D plotting method uses viscous hydrogels
[38]
melting process include fused deposition modelling which are initially loaded in a syringe and injected through
(FDM), precise extrusion manufacturing (PEM), a micro-needle used as the extrusion nozzle into a liquid
multiphase jet solidification (MJS), precision extrusion solution with a density similar to that of the hydrogel.
deposition (PED), and 3D fiber deposition [31–34] . FDM The hydrogel from a pressurized syringe can be deposited
technique is the most commonly used nozzle based 3D as a single continuous microstrand or as individual
Figure 2. Schematic images of (A) nozzle and (B) inkjet printer based hydrogel 3D printing systems. (reproduced with permission from [1].
Copyright 2017, Elsevier Ltd)
International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 1 5