Page 82 - IJB-4-1
P. 82
Liang H, et al.
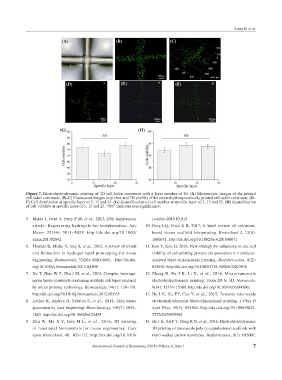
(A) (B) (C)
(D) (E) (F)
(G) (H)
Figure 7. Electrohydrodynamic printing of 3D cell-laden constructs with a layer number of 30. (A) Microscopic images of the printed
cell-laden constructs. (B–C) Fluorescent images (top view and 3D profile) of the electrohydrodynamically printed cell-laden constructs. (D–
F) Cell distribution at specific layer of 5, 15 and 25. (G) Quantification of cell number at specific layer of 5, 15 and 25. (H) Quantification
of cell viability at specific layer of 5, 15 and 25. “NS” indicates non-significance.
5. Malda J, Jetze V, Ferry P M, et al., 2013, 25th Anniversary j.copbio.2016.03.014
article: Engineering hydrogels for biofabrication. Adv 10. Ning LQ, Chen X B, 2017, A brief review of extrusion-
Mater, 25(36): 5011–5028. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ based tissue scaffold bio-printing. Biotechnol J, 12(8):
adma.201302042 1600671. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/biot.201600671
6. Thomas B, Mieke V, Jorg S, et al., 2012, A review of trends 11. Koo Y, Kim G, 2016, New strategy for enhancing in situ cell
and limitations in hydrogel-rapid prototyping for tissue viability of cell-printing process via piezoelectric transducer-
engineering. Biomaterials, 33(26): 6020–6041. http://dx.doi. assisted three-dimensional printing. Biofabrication, 8(2):
org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.050 025010. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/8/2/025010
7. Xu T, Zhao W Z, Zhu J M, et al., 2013, Complex het ero ge- 12. Zhang B, He J K, Li X, et al., 2016, Micro/nanoscale
neous tissue constructs containing multiple cell types prepared electrohydrodynamic printing: From 2D to 3D. Nanoscale,
by inkjet printing technology. Biomaterials, 34(1): 130–139. 8(34): 15376–15388. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c6nr04106j
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.035 13. He J K, Xu FY, Cao Y, et al., 2015, Towards microscale
8. Lothar K, Andrea D, Sabrina S, et al., 2012, Skin tissue electrohydrodynamic three-dimensional printing. J Phys D
generation by laser bioprinting. Biotechnology, 109(7): 1855– Appl Phys, 49(5): 055504. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0022-
1863. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bit.24455 3727/49/5/055504
9. Zhu W, Ma X Y, Gou M L, et al., 2016, 3D printing 14. He J K, Xu F Y, Dong R N, et al., 2016, Electrohydrodynamic
of func tion al biomaterials for tissue engineering. Curr 3D printing of microscale poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffolds with
Opin Bio technol, 40: 103–112. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/ multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Biofabrication, 9(1): 015007.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2018)–Volume 4, Issue 1 7