Page 144 - IJB-10-4
P. 144
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing innovations against infection
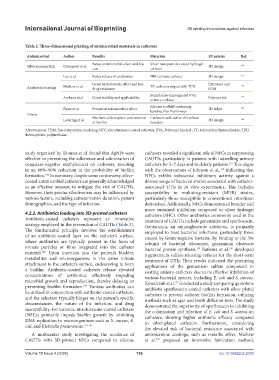
Table 2. Three-dimensional printing of antimicrobial materials in catheters
Antimicrobial Author Benefits Materials 3D printer Ref.
Better antimicrobial effect and low Silver nanoparticle coated hydrogel
Silver nanoparticle Davenport et al. 3D design 146
cost catheter
Lee et al. Better release of antibiotics NFC urinary catheter 3D design 175
Good bacteriostatic effect and less Extrusion and
Antibiotics loading Mathew et al. drug resistance TC catheters doped with TPU FDM 158
Secnidazole-impregnated PVA
Archana et al. Good stability and applicability Polymer ink 159
urinary catheter
Silicone scaffold containing
Kyser et al. Persistent antimicrobial effect lactobacillus rhamnosus 3D inkjet 162
Others
Levering et al. Mechanical disruption and removal Catheters with active dirt release 3D design 164
of biofilm function
Abbreviations: FDM, fused deposition modeling; NFC, nitrofurazone-coated catheters; PVA, Polyvinyl Alcohol ; TC, tetracycline hydrochloride; TPU,
thermoplastic polyurethane.
study organized by Thomas et al. found that AgNPs were catheters revealed a significant role of NFCs in suppressing
effective in preventing the adherence and colonization of CAUTIs, particularly in patients with indwelling urinary
coagulase-negative staphylococci on catheters, resulting catheters for 5–7 days and in elderly patients. This aligns
153
in an 80%–90% reduction in the probability of biofilm with the observations of Johnson et al., indicating that
154
formation. In summary, despite some controversy, silver- NFCs exhibit substantial inhibitory activity against a
148
coated antimicrobial catheters are generally acknowledged diverse range of bacterial strains associated with catheter-
as an effective measure to mitigate the risk of CAUTIs. associated UTIs in in vitro experiments. This includes
However, their precise effectiveness may be influenced by susceptibility to multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains,
various factors, including catheterization duration, patient particularly those susceptible to conventional nitrofuran
demographics, and the type of infection. derivatives. Additionally, NFCs demonstrated broader and
more sustained inhibition compared to silver hydrogel
4.2.2. Antibiotics loading into 3D-printed catheters catheters (SHC). Other antibiotics commonly used in the
Antibiotic-coated catheters represent an innovative treatment of CAUTIs include gentamicin and sparfloxacin.
strategy employed in the prevention of CAUTIs (Table 2). Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, is primarily
The fundamental principle involves the establishment employed to treat bacterial infections, particularly those
of an antibiotic-coated layer on the catheter’s surface, caused by Gram-negative bacteria. By binding to the 30s
where antibiotics are typically present in the form of subunit of bacterial ribosomes, gentamicin obstructs
minute particles or films integrated into the catheter bacterial protein synthesis. Rafienia et al. developed
156
155
149
material. Upon insertion into the patient’s bladder, a gentamicin sulfate-releasing catheter for the short-term
metabolites and microorganisms in the urine initiate treatment of UTIs. Their results indicated the promising
attachment to the catheter’s surface, endeavoring to form applications of the gentamicin sulfate compound in
a biofilm. Antibiotic-coated catheters release elevated coating urinary catheters due to its effective inhibition of
concentrations of antibiotics, effectively impeding various bacterial species, including E. coli and S. aureus.
microbial growth and reproduction, thereby delaying or Kowalczuk et al. conducted a study comparing quinolone
157
preventing biofilm formation. Various antibiotics can antibiotic sparfloxacin-coated catheters with silver-plated
150
be utilized in conjunction with antibiotic-coated catheters, catheters to prevent catheter biofilm formation, utilizing
and the selection typically hinges on the patient’s specific methods such as agar and broth diffusion tests. The study
circumstances, the nature of the infection, and drug demonstrated the superiority of sparfloxacin in inhibiting
susceptibility. For instance, nitrofurazone-coated catheters the colonization and infection of E. coli and S. aureus on
(NFCs) primarily impede biofilm growth by inhibiting catheters, showing higher antibiotic efficacy compared
DNA replication in microorganisms such as S. aureus, E. to silver-plated catheters. Furthermore, considering
coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. 151,152
the elevated risk of bacterial resistance associated with
A multicenter study investigating the incidence of antimicrobial coatings, such as metallic silver, Mathew
CAUTIs with 3D-printed NFCs compared to silicone et al. proposed an innovative fabrication method,
158
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 136 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2338