Page 282 - IJB-10-4
P. 282
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing prosthesis for palatal fistula
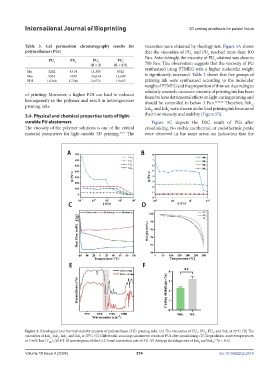
Table 3. Gel permeation chromatography results for viscosities were obtained by rheology test. Figure 5A shows
polyurethanes (PUs) that the viscosities of PU and PU reached more than 100
1
2
Pa·s. Astonishingly, the viscosity of PU attained was close to
PU 1 PU 2 PU 3 PU 3 3
(R = 2) (R = 2.5) 700 Pa·s. This observation suggests that the viscosity of PU
Mn 3262 4314 11,385 6920 synthesized using PTMEG with a higher molecular weight
Mw 5333 7438 23,654 13,609 is significantly increased. Table 3 shows that five groups of
PDI 1.6348 1.7240 2.0776 1.9665 printing ink were synthesized according to the molecular
weight of PTMEG and the proportion of thinner. According to
scholarly research, excessive viscosity of printing ink has been
of printing. Moreover, a higher PDI can lead to reduced found to have detrimental effects on light-curing printing and
homogeneity in the polymer and result in heterogeneous should be controlled to below 3 Pa·s. 34,42,43 Therefore, Ink ,
printing inks. Ink , and Ink were chosen as the final printing ink because of
1
4
2
3.4. Physical and chemical properties tests of light- their low viscosity and stability (Figure 5B).
curable PU elastomers Figure 5C depicts the DSC result of PUs after
The viscosity of the polymer solutions is one of the critical crosslinking. No visible exothermic or endothermic peaks
material parameters for light-curable 3D printing. 34,41 The were observed in the same areas, an indication that the
Figure 5. Rheological and thermal stability analysis of polyurethane (PU) printing inks. (A) The viscosities of PU , PU , PU , and Ink at 25°C. (B) The
2
3
1
5
viscosities of Ink , Ink , Ink , and Ink at 25°C. (C) Differential scanning calorimetry results of PUs after crosslinking. (D) Degradation onset temperatures
2
1
4
3
at 5 wt% loss (T ). (E) FT-IR spectrogram of the C=C bond conversion rate of PU. (F) Average shrinkage rate of Ink and Ink ; **p < 0.01.
5% 2 4
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 274 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2516