Page 21 - IJB-10-5
P. 21
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting for nanoparticle evaluation
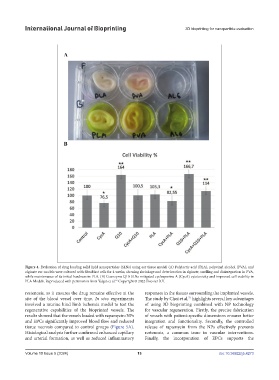
Figure 4. Evaluation of drug loading solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) using ear tissue model. (A) Polylactic acid (PLA), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and
alginate ear models were cultured with fibroblast cells for 4 weeks, showing shrinkage and deterioration in alginate, swelling and disintegration in PVA,
while maintenance of its initial hardness in PLA. (B) Coenzyme Q10-SLNs mitigated cyclosporine A (CycA) cytotoxicity and improved cell viability in
PLA Models. Reproduced with permission from Yalgın et al. Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V.
62
restenosis, as it ensures the drug remains effective at the responses in the tissues surrounding the implanted vessels.
site of the blood vessel over time. In vivo experiments The study by Choi et al. highlights several key advantages
71
involved a murine hind limb ischemia model to test the of using 3D bioprinting combined with NP technology
regenerative capabilities of the bioprinted vessels. The for vascular regeneration. Firstly, the precise fabrication
results showed that the vessels loaded with rapamycin-NPs of vessels with patient-specific dimensions ensures better
and EPCs significantly improved blood flow and reduced integration and functionality. Secondly, the controlled
tissue necrosis compared to control groups (Figure 5A). release of rapamycin from the NPs effectively prevents
Histological analysis further confirmed enhanced capillary restenosis, a common issue in vascular interventions.
and arterial formation, as well as reduced inflammatory Finally, the incorporation of EPCs supports the
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 13 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4273