Page 248 - IJB-10-5
P. 248
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed hydrogels for tumor therapy
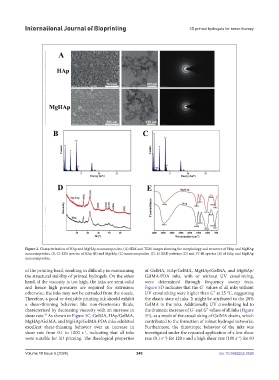
Figure 2. Characterization of HAp and MgHAp nanocomposites. (A) SEM and TEM images showing the morphology and structure of HAp and MgHAp
nanocomposites. (B, C) EDS spectra of HAp (B) and MgHAp (C) nanocomposites. (D, E) XRD patterns (D) and FT-IR spectra (E) of HAp and MgHAp
nanocomposites.
of the printing head, resulting in difficulty in maintaining of GelMA, HAp/GelMA, MgHAp/GelMA, and MgHAp/
the structural stability of printed hydrogels. On the other GelMA-PDA inks, with or without UV crosslinking,
hand, if the viscosity is too high, the inks are semi-solid were determined through frequency sweep tests.
and hence high pressures are required for extrusion; Figure 5D indicates that the G´ values of all inks without
otherwise, the inks may not be extruded from the nozzle. UV crosslinking were higher than G˝ at 25 °C, suggesting
Therefore, a good or desirable printing ink should exhibit the elastic state of inks. It might be attributed to the 20%
a shear-thinning behavior, like non-Newtonian fluids, GelMA in the inks. Additionally, UV crosslinking led to
characterized by decreasing viscosity with an increase in the dramatic increase of G´ and G˝ values of all inks (Figure
shear rate. As shown in Figure 5C, GelMA, HAp/GelMA, 5E), as a result of the crosslinking of GelMA chains, which
49
MgHAp/GelMA, and MgHAp/GelMA-PDA inks exhibited contributed to the formation of robust hydrogel networks.
excellent shear-thinning behavior over an increase in Furthermore, the thixotropic behavior of the inks was
shear rate from 0.1 to 1000 s , indicating that all inks investigated under the repeated application of a low shear
−1
were suitable for 3D printing. The rheological properties rate (0.1 s ) for 120 s and a high shear rate (100 s ) for 60
−1
−1
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 240 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3526