Page 41 - IJB-10-5
P. 41
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinted tumor immune microenvironment
3. Immune cells and their social differentiation of DCs. 28,29 This leads to impaired antigen
30
interactions in TIME presentation and consequently reduces T cell activation.
Immunosuppressive cytokines can induce the conversion
TIME consists of a tumor, ECM, vascular network and a of macrophages from anti-tumor (M1-like) to pro-
variety of stromal cells and immune cells (Figure 1). The tumor (M2-like) phenotypes, thereby supporting tumor
21
main immune cells involved in the TIME are cytotoxic T growth and metastasis. M2 macrophages also express
26
lymphocytes (CTLs), dendritic cells (DCs), macrophages, checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, which can bind to
and natural killer (NK) cells, which interact with each PD-1 on T cells, leading to T cell exhaustion and reduced
other within this complex environment (Table 1). T cells anti-tumor activity. 31
play a critical role in the immune response against various
cancers. Notably, CTLs can kill cancer cells directly when 4. Bioprinting the TIME
22
properly activated. Upon recognizing a tumor cell, CTLs 4.1. Components for bioprinting the TIME
release perforin and granzymes, which induce apoptosis in
the tumor cell. Additionally, T cells secrete cytokines such 4.1.1. Source of immune cells
23
as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor Immune cells can be derived from commercial sources,
alpha (TNF-α), which not only have direct anti-tumor patient biopsies, or generated from induced pluripotent
effects but also recruit and activate other immune cells. stem cells (iPSCs) to model specific immune responses.
24
DCs are key antigen-presenting cells that play a crucial
role in initiating and regulating immune responses. Immune cells extracted from mice or humans are
25
Macrophages are frequently observed in several solid widely used in research to study immune responses in
37
tumors, making them a common choice for modeling the TIME in vitro. Mouse-derived immune cells, such as
bTIME. NK cells secrete cytokines such as IFN-γ, which those from the spleen, lymph nodes, or bone marrow, have
26
have anti-tumor effects and can modulate the activity been utilized extensively in preclinical models. However,
of other immune cells, enhancing the overall immune there are species-specific differences in immune responses
that may not fully replicate human immune responses
response against the tumor.
27
due to differences in immune system architecture and
However, tumors secrete various immunosuppressive function between species. 38,39 Human-derived immune
cytokines, which interfere with the normal activity of cells offer high authenticity for modeling human diseases
immune cells. For example, these cytokines inhibit the and testing therapies. Variability among donors can
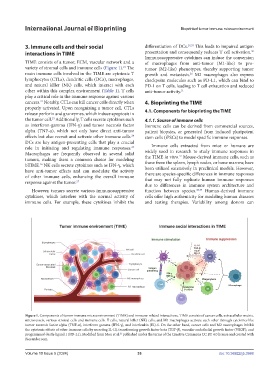
Figure 1. Components of tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) and immune-related interactions. TIME consists of cancer cells, extracellular matrix,
microvessels, various stromal cells and immune cells. T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and M1 macrophages activate each other through cytokines like
tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interferon gamma (IFN-γ), and interleukin (IL)-6. On the other hand, cancer cells and M2 macrophages inhibit
the cytotoxic effects of other immune cells by secreting IL-10, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and
programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). Modified from Mou et al. published under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license and created with
21
Biorender.com.
Volume 10 Issue 5 (2024) 33 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3988