Page 18 - IJB-6-1
P. 18
Digital light processing based 3D printing for medical applications
little cell damage. When light is projected onto printing platform. This platform can fabricate
the resin using DLP technology, instead of being multiscale vascular channels, ranging from the
restricted to a spot like the laser-assisting 3D main trunk channel (> 1100 μm wide) to the
printing, the entire layer is printed immediately. relatively small branch channel (up to 17 μm
Hence, this technology allows fast printing [5,12] . wide) . Saha et al. combined the advantages of
[17]
two-photon lithography (TPL) and DLP printing
2.2 The advancements of DLP-based 3D and developed a femtosecond projection TPL
printing
(FP-TPL) technique. By this method, complex 3D
During the past decade, the printing accuracy structures maintaining sub-500-nm features can
[18]
which is, a key indicator of 3D printing be printed rapidly .
technology, has improved greatly. The accuracy Besides accuracy, many methods were applied
improvement is related to the printing equipment, to improve printing speed. These methods greatly
materials, and process parameters. When DLP 3D improve printing efficiency and ensure cell
[19]
printing technology was first invented in 2006, viability during tissue construction . In 2015,
the researchers manufactured constructs that John et al. modified the technique and created a
have 20 μm microstructure . In 2013, Yi et al. continuous liquid interface fabrication method. The
[12]
fabricated constructs with various topologies. In continuous liquid interface in this study is realized
fact, the resolution of DLP 3D printing partially through the oxygen-permeating region under
depends on the material chosen. When the 3D the printing platform, which forms a persistent
constructs are printed using polyethylene glycol liquid interface between the oxygen-permeating
diacrylate (PEGDA MW = 700 da) solely, the XY region and the photopolymerization region of the
resolution of the constructs can reach nearly 6 by material, in which the material cannot conduct
6 μm. Meanwhile, the resolution is about 17 μm photopolymerization. When the average thickness
with bioink containing 10% gelatin-methacrylate of each layer is set at 50–100 μm, this method
(GelMA) and 3 × 10 cells/mL . Dai et al. can manufacture a 3D structure with 5 cm high
[16]
6
used a high precision DMD (each micromirror in <10 min . Recently, a faster DLP 3D printing
[20]
is 10.8 μm) to build the projection-based 3D method, computed axial lithography, has been
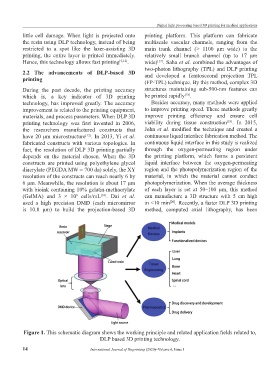
Figure 1. This schematic diagram shows the working principle and related application fields related to,
DLP based 3D printing technology.
14 International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1