Page 71 - IJB-6-1
P. 71
Lee, et al.
be generated to partially or fully encapsulate 2.2 Use of build/support strategies in bioprinting
the 3D-printed part commonly used in material
jetting and material extrusion techniques [33,34] . Bioprinting allows the deposition of heterogeneous
Support structures are also generated in response materials and cells in a controlled manner to form an
to include technology-specific consideration. engineered construct that recaptures the complexities
For instance, the support structure in selective of native tissues [25,48,49] . The capability of depositing
laser melting [35-38] or electron-beam melting multimaterial in bioprinting is in line with build/
[39]
functions is strategically placed to improve heat support strategies commonly found in 3D printing.
dissipation and prevent print jobs from thermal Increasing research interest lies in bioprinting
warping . cell-hydrogel materials using a build/support
[32]
The prevalence of multimaterial deposition configuration [4,50-56] . In build/support configuration,
and build/support printing configuration has been support materials are used to provide mechanical
demonstrated across additive manufacturing strength to hold the structure giving the overall form
technologies (Table 1). With an increase interest for the engineered construct. In many cases, these
in multimaterial bioprinting for use in build- materials are eventually removed from the printed
support configuration, it is imperative to develop a constructed (i.e., sacrificial). On the other hand,
systematic framework for file processing method cells and/or hydrogels (build materials) provide the
in multimaterial bioprinting. Considerations in functional components in the bioprinted construct.
segmenting computer-aided design (CAD) files Such printing strategy can be either vat-based
for bioprinting are also discussed in the following or sequential printing of build/support materials
section. (Figure 1). In such build/support configuration, the
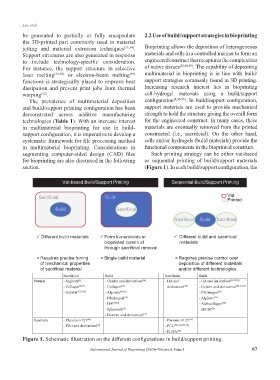
Vat-based Build/Support Printing Sequential Build/Support Printing
Sacrificial Build Vat
Printed
Build Sacrificial
Sacrificial Build Sacrificial
Different build materials Form lumen/voids in Different build and sacrificial
bioprinted construct materials
through sacrificial removal
Requires precise tuning Single build material Requires precise control over
of mechanical properties deposition of different materials
of sacrificial material and/or different technologies
Sacrificial Build Sacrificial Build
Natural - Alginate [4] - Gelatin and derivatives [46] - HA and - HA and derivatives [44,52,54]
- Collagen [4,47] - Collagen [56] derivatives [44] - Gelatin and derivatives [44,52,54]
- Gelatin [47,55,56] - Alginate [47,56] - Fibrinogen [54]
- Fibrinogen [47] - Alginate [51]
- HA [47,56] - Atelocollagen [52]
- Spheroids [55] - dECM [58]
- Dextran and derivatives [57]
Synthetic - Pluronic F127 [46] - Pluronic F127 [54]
- PEO and derivatives [57] - PCL [46,51,52,54,58]
- PLGA [52]
Figure 1. Schematic illustration on the different configurations in build/support printing.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1 67