Page 41 - IJB-6-2
P. 41
Chen, et al.
scaffolds exhibited smooth and dense surfaces vaterite or calcite. In a Ca -gelatin bath, HAc-
2+
(Figure 3A-F). The high-resolution SEM image Alg undergoes ionic crosslinking, whereby
of HAc-Alg indicated the presence of spherical calcium carbonate is formed through the reaction
nanoparticles with sizes ranging from five to between calcium and carbonate ions. Carbonate
a few tens of nanometers on the nanoporous ions are known to exist in aqueous solution due
polymeric network (Figure 3C). In contrast, to the dissolved carbon dioxide [24] . Hosoda and
the HAc-Alg/CaP hydrogel exhibited densely Kato previously demonstrated the formation of
packed nanoparticles that formed a continuous a thin calcium carbonate crystalline layer in a
2+
mineral network throughout the printed scaffold reactive Ca -containing solution in the presence
(Figure 3D). of insoluble and soluble acidic polymers with
The increased CaP content (from 10 wt% to 30 carboxyl groups [25] . The HAc-Alg units inside
wt%) was caused by the increased number of CaP the gelatin bath should act as insoluble acidic
particles and not the crystal growth of nanoparticles polymers and soluble acidic biomacromolecules,
(Supplementary Figure 2 and Supplementary allowing calcium carbonate crystals to grow
Table 1). The nucleation rate of nanoparticle on the polymer matrix. Due to the interactions
formation is often experimentally described in between the calcium ions and carboxyl groups,
terms of supersaturation of the solution (S), free the localized calcium concentration around
surface energy (γ) of particles and temperature (T) the HAc-Alg matrix is likely to induce crystal
as follows, where A and C are constants : growth.
[23]
dN Aexp C ( 3 ) A
3
dt TlnS 2 (4)
According to Eq. (4), the total number of CaP
nuclei should be significantly larger for 30 wt% CaP
compared with 10 wt% CaP at room temperature,
due to the higher level of supersaturation induced
by increased phosphate ions in the presence
of excess calcium ions (assuming that the
CaP of both systems has the same free surface B
energy) . Meanwhile, the total reaction time was
[23]
limited to 20 min, which constrained the growth
of nanoparticles. As a result, CaP nanoparticles
for HAc-Alg/30 wt% CaP formed the continuous
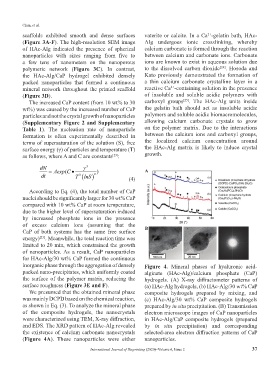
inorganic phase through the aggregation of densely Figure 4. Mineral phases of hyaluronic acid-
packed nano-precipitates, which uniformly coated alginate (HAc-Alg)/calcium phosphate (CaP)
the surface of the polymer matrix, reducing the hydrogels. (A) X-ray diffractometer patterns of
surface roughness (Figure 3E and F). (a) HAc-Alg hydrogels, (b) HAc-Alg/30 wt% CaP
We presumed that the obtained mineral phase composite hydrogels prepared by mixing, and
was mainly DCPD based on the chemical reaction, (c) HAc-Alg/30 wt% CaP composite hydrogels
as shown in Eq. (3). To analyze the mineral phase prepared by in situ precipitation. (B) Transmission
of the composite hydrogels, the nanocrystals electron microscope images of CaP nanoparticles
were characterized using TEM, X-ray diffraction, in HAc-Alg/CaP composite hydrogels (prepared
and EDS. The XRD pattern of HAc-Alg revealed by in situ precipitation) and corresponding
the existence of calcium carbonate nanocrystals selected-area electron diffraction patterns of CaP
(Figure 4A). These nanoparticles were either nanoparticles.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 2 37