Page 106 - IJB-10-6
P. 106
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed bioelectronic devices
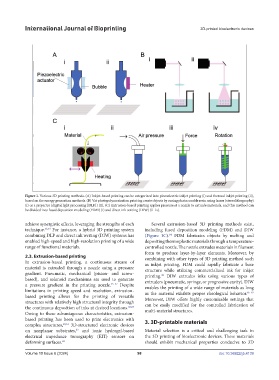
Figure 1. Various 3D printing methods. (A) Inkjet-based printing can be categorized into piezoelectric inkjet printing (i) and thermal inkjet printing (ii),
based on the energy generation methods. (B) Vat photopolymerization printing create objects by curing photocurable resin using lasers (stereolithography)
(i) or a projector (digital light processing [DLP]) (ii). (C) Extrusion-based printing applies pressure at a nozzle to extrude materials, and this method can
be divided into fused deposition modeling (FDM) (i) and direct ink writing (DIW) (ii–iv).
achieve synergistic effects, leveraging the strengths of each Several extrusion-based 3D printing methods exist,
technique. 53,54 For instance, a hybrid 3D printing system including fused deposition modeling (FDM) and DIW
combining DLP and direct ink writing (DIW) systems has (Figure 1C). FDM fabricates objects by melting and
64
enabled high-speed and high-resolution printing of a wide depositing thermoplastic materials through a temperature-
range of functional materials. controlled nozzle. The nozzle extrudes materials in filament
form to produce layer-by-layer elements. Moreover, by
2.3. Extrusion-based printing combining with other types of 3D printing method such
In extrusion-based printing, a continuous stream of as inkjet printing, FDM could rapidly fabricate a base
material is extruded through a nozzle using a pressure structure while utilizing commercialized ink for inkjet
gradient. Pneumatic, mechanical (piston- and screw- printing. DIW extrudes inks using various types of
30
based), and solenoid mechanisms are used to generate extruders (pneumatic, syringe, or progressive cavity). DIW
a pressure gradient in the printing nozzle. 55–57 Despite enables the printing of a wide range of materials as long
limitations in printing speed and resolution, extrusion- as the material exhibits proper rheological behavior. 65–67
based printing allows for the printing of versatile Moreover, DIW offers highly customizable settings that
structures with relatively high structural integrity through can be easily modified for the controlled fabrication of
the continuous deposition of inks at desired locations. 58,59
Owing to these advantageous characteristics, extrusion- multi-material structures.
based printing has been used to print electronics with 3. 3D-printable materials
complex structures, 60,61 3D-structured electronic devices
on nonplanar substrates, and ionic hydrogel-based Material selection is a critical and challenging task in
62
electrical impedance tomography (EIT) sensors on the 3D printing of bioelectronic devices. These materials
deforming surfaces. should exhibit mechanical properties conducive to 3D
63
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 98 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4139