Page 105 - IJB-10-6
P. 105
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed bioelectronic devices
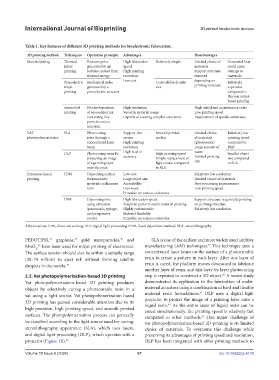
Table 1. Key features of different 3D printing methods for bioelectronic fabrication.
3D printing method Techniques Operation principle Advantages Disadvantages
Material jetting Thermal Pressure pulse High fabrication Relatively simple Limited choice of Generated heat
inkjet generated by air speed materials could cause
printing bubbles created from High printing Support structure damage to
thermal energy resolution required materials
Piezoelectric Mechanical pulse Low cost Controllable droplet depending on Relatively
inkjet generated by a size printing structure expensive
printing piezoelectric actuator compared to
thermal inkjet-
based printing
Aerosol jet Precise deposition High resolution High initial and maintenance costs
printing of aerosolized ink Versatile material usage Low printing speed
containing fine Capable of creating complex structures Requirement of specific substrates
particles onto a
substrate
VAT SLA Photocuring Support-free Smooth printed Limited choice Relatively low
photopolymerization resin through a system surface of materials printing speed
concentrated laser High printing (photoresins) compared to
beam resolution Large amount of DLP
DLP Photocuring resin by High level of High printing speed waste Smaller object
projecting an image accuracy Simple replacement of Limited printing size compared
of a printing layer light source compared size to SLA
onto the resin to SLA
Extrusion-based FDM Depositing melted Low cost Relatively low resolution
printing thermoplastic Large object size Limited choice of materials
materials in filament Accessibility Post-processing requirements
form Less waste Low printing speed
Printable on various substrates
DIW Depositing inks High fabrication speed Support structure required depending
using extruders Simple to perform multi-material printing on printing structure
(pneumatic, syringe, Highly customizable Relatively low resolution
and progressive Material flexibility
cavity) Printable on various substrates
Abbreviations: DIW, direct ink writing; DLP, digital light processing; FDM, fused deposition method; SLA, stereolithography.
PEDOT:PSS, graphene, gold nanoparticles, and SLA is one of the earliest and most widely used additive
45
44
43
MnO , have been used for inkjet printing of electronics. manufacturing (AM) techniques. This technique uses a
49
46
2
The surface tension should also be within a suitable range concentrated laser beam on the surface of a photocurable
(30–70 mN/m) to eject ink without forming satellite resin to create a pattern in each layer. After one layer of
droplets in the nozzle. 47 resin is cured, the platform moves downward to fabricate
another layer of resin, and this layer-by-layer photocuring
50
2.2. Vat photopolymerization-based 3D printing step is repeated to construct a 3D object. A recent study
Vat photopolymerization-based 3D printing produces demonstrated its application in the fabrication of multi-
objects by selectively curing a photocurable resin in a material actuators using a combination of hard and flexible
51
vat using a light source. Vat photopolymerization-based material resin formulations. DLP uses a digital light
3D printing has gained considerable attention due to its projector to project the image of a printing layer onto a
liquid resin. As the entire layer of liquid resin can be
48
high precision, high printing speed, and smooth printed cured simultaneously, the printing speed is relatively fast
surfaces. The photopolymerization process can generally compared to other methods. One major challenge of
52
be classified according to the light source used for curing: vat photopolymerization-based 3D printing is its limited
stereolithography appearance (SLA), which uses lasers, choice of materials. To overcome this challenge while
and digital light processing (DLP), which operates with a preserving its advantages of printing speed and resolution,
projector (Figure 1B). 48 DLP has been integrated with other printing methods to
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 97 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4139