Page 184 - IJB-10-6
P. 184
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed EVs for nasal septal defects
temporary support, with PLGA nanofilaments arranged after the particles had completely dissolved. The high-
in an extracellular matrix fiber-like pattern to provide voltage power supply was connected to the positive point
directional cell adhesion and growth sites. This composite of the discharge port; the receiver was connected to the
hydrogel scaffold addresses the issue of EV injection loss by negative point of the high-voltage power supply; the voltage
enabling slow release over an extended period, enhancing was set to 16 kV; the distance between the discharge port
repair efficacy. After comparing the effects of 2D and 3D and the receiver was set to 17.5 cm; and the discharge flow
EVs on chondrocyte function, we investigate the effect rate of the solution was set to 15 μL/ min. The biofilm was
of different concentrations of 3D EVs on chondrocyte collected after electrospinning for 2 h using a 5 mL syringe
proliferation, migration, and extracellular matrix with an 18-G needle, and the biofilm was incubated in
production. Additionally, we constructed an in vivo model a 37°C drying oven overnight to obtain the materials
of nasal septal defect in rabbits and implanted biological required for the experiment.
scaffolds with or without EVs into the rabbits to explore The composite scaffold is mainly composed of a
the potential of EVs for tissue repair. The comprehensive combination of GelMA hydrogel and PLGA scaffold. Based
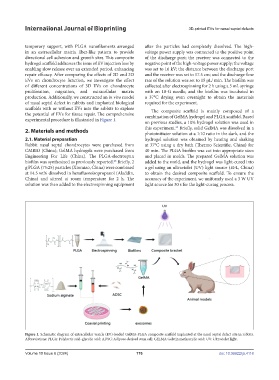
experimental procedure is illustrated in Figure 1. on previous studies, a 10% hydrogel solution was used in
29
2. Materials and methods this experiment. Briefly, solid GelMA was dissolved in a
photoinitiator solution at a 1:10 ratio in the dark, and the
2.1. Material preparation hydrogel solution was obtained by heating and shaking
Rabbit nasal septal chondrocytes were purchased from at 37°C using a dry bath (Thermo Scientific, China) for
CMBIO (China); GelMA hydrogels were purchased from 40 min. The PLGA biofilm was cut into appropriate sizes
Engineering For Life (China). The PLGA-electrospun and placed in molds. The prepared GelMA solution was
biofilm was synthesized as previously reported. Briefly, 2 added to the mold, and the hydrogel was light-cured into
28
g PLGA (75:25) particles (Xinmiao, China) were combined a gel using an ultraviolet (UV) light source (EFL, China)
at 14.5 wt% dissolved in hexafluoroisopropanol (Aladdin, to obtain the desired composite scaffold. To ensure the
China) and stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The accuracy of the experiment, we uniformly used a 3 W UV
solution was then added to the electrospinning equipment light source for 30 s for the light-curing process.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of extracellular vesicle (EV)-loaded GelMA-PLGA composite scaffold implanted at the nasal septal defect site in rabbits.
Abbreviations: PLGA: Polylactic acid-glycolic acid; ADSC: Adipose-derived stem cell; GELMA Gelatin methacrylic acid; UV: Ultraviolet light.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 176 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4118