Page 189 - IJB-10-6
P. 189
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed EVs for nasal septal defects
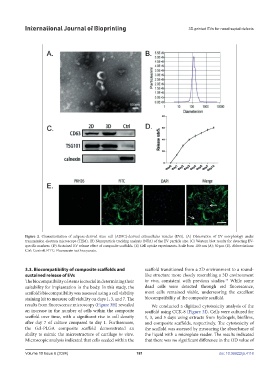
Figure 2. Characterization of adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC)-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). (A) Observation of EV morphology under
transmission electron microscope (TEM). (B) Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of the EV particle size. (C) Western blot results for detecting EV-
specific markers. (D) Sustained EV release effect of composite scaffolds. (E) Cell uptake experiments. Scale bars: 100 nm (A); 50 μm (E). Abbreviations:
Ctrl: Control; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate.
3.3. Biocompatibility of composite scaffolds and scaffold transitioned from a 2D environment to a round-
sustained release of EVs like structure more closely resembling a 3D environment
35
The biocompatibility of stents is crucial in determining their in vivo, consistent with previous studies. While some
suitability for implantation in the body. In this study, the dead cells were detected through red fluorescence,
scaffold’s biocompatibility was assessed using a cell viability most cells remained viable, underscoring the excellent
staining kit to measure cell viability on days 1, 3, and 7. The biocompatibility of the composite scaffold.
results from fluorescence microscopy (Figure 3H) revealed We conducted a digitized cytotoxicity analysis of the
an increase in the number of cells within the composite scaffold using CCK-8 (Figure 3I). Cells were cultured for
scaffold over time, with a significant rise in cell density 1, 3, and 5 days using extracts from hydrogels, biofilms,
after day 7 of culture compared to day 1. Furthermore, and composite scaffolds, respectively. The cytotoxicity of
the Gel-PLGA composite scaffold demonstrated an the scaffold was assessed by measuring the absorbance of
ability to mimic the microstructure of cartilage in vitro. the liquid with a microplate reader. The results indicated
Microscopic analysis indicated that cells seeded within the that there was no significant difference in the OD value of
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 181 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4118