Page 192 - IJB-10-6
P. 192
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed EVs for nasal septal defects
contrary to previous findings that suggested higher EV high concentration of EVs exerts an inhibitory effect on
concentrations would increase cell proliferation rates. 37 cell migration.
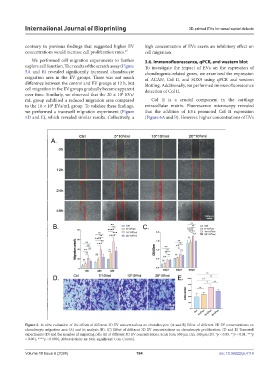
We performed cell migration experiments to further 3.6. Immunofluorescence, qPCR, and western blot
explore cell function. The results of the scratch assay (Figure To investigate the impact of EVs on the expression of
5A and B) revealed significantly increased chondrocyte chondrogenic-related genes, we examined the expression
migration area in the EV groups. There was not much of ACAN, Col II, and SOX9 using qPCR and western
difference between the control and EV groups at 12 h, but blotting. Additionally, we performed immunofluorescence
cell migration in the EV groups gradually became apparent detection of Col II.
over time. Similarly, we observed that the 20 × 10 EVs/
8
mL group exhibited a reduced migration area compared Col II is a crucial component in the cartilage
to the 10 × 10 EVs/mL group. To validate these findings, extracellular matrix. Fluorescence microscopy revealed
8
we performed a transwell migration experiment (Figure that the addition of EVs promoted Col II expression
5D and E), which revealed similar results. Collectively, a (Figure 6A and B). However, higher concentrations of EVs
Figure 5. In vitro evaluation of the effects of different 3D EV concentrations on chondrocytes. (A and B) Effect of different 3D EV concentrations on
chondrocyte migration area (A) and its analysis (B). (C) Effect of different 3D EV concentrations on chondrocyte proliferation. (D and E) Transwell
experiments (D) and the number of migrating cells (E) at different 3D EV concentrations. Scale bars: 500 μm (A); 100 μm (D). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p
< 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: ns: Non-significant; Con: Control.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 184 doi: 10.36922/ijb.4118