Page 21 - IJB-7-2
P. 21
Zhang, et al.
AM is a novel manufacturing technology applied to blades, or knives, while fluidization-based technology
various materials and is considered one of the most advanced deposits powder through one or more nozzles that feed the
manufacturing technologies . AM can overcome PM- powder directly into the laser focus. Figures 2 and 3 show
[30]
related impurity issues such as O and N inclusion. For the SLM and DED processes, respectively.
2
2
example, the SLM chamber has an inert argon atmosphere, Considering the relatively low accuracy of DED
which can significantly avoid any possible contamination technology, powder bed fusion technology is more prevalent
such as impurity gas and Ni evaporation . For electron when manufacturing complex microstructures. EBM can
[29]
beam melting (EBM), its vacuum environment is also be used as an essential technology for the production of
conducive to reducing impurity gas . AM technology metallic biomedical materials. Wang et al. [22,33] conducted
[31]
can be divided into powder bed-based technology, such a series of studies on the production of Ti-6Al-4V by
as selective laser melting (SLM) and electron beam EBM. Few reports are available regarding EBM-NiTi [34-36] .
melting (EBM), or fluidization-based technology, such as The high vacuum conditions of EBM are suitable for
directed energy deposition (DED) . Powder bed-based reactive materials such as NiTi . However, due to poor
[32]
[37]
technology processes powder deposition through rollers, surface roughness, the fatigue performance of EBM parts
is terrible . Furthermore, the preheating stage of EBM
[38]
is not suitable for preparing NiTi . Therefore, this paper
[39]
reviews the recent developments of AM-NiTi, especially
SLM-NiTi, as orthopedic implants, the porous structure
design, and mechanical properties. Furthermore, the
relationship between SLM-NiTi properties and various
influencing factors and the characterization methods
for AM-NiTi implants are also summarized and finally,
current challenges were discussed.
2. Influencing factors in SLM-NiTi
production
For metallic AM in biomedical applications, powder bed-
based technology is much more prevalent in creating
complex geometry . Due to its high resolution, the
[25]
most common manufacturing method to produce NiTi
is SLM. The production process for SLM utilization in
NiTi includes three main factors: powder preparation,
processing parameters, and gas atmosphere . In terms of
[42]
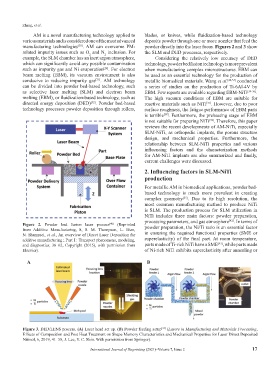
Figure 2. Powder bed fusion laser process (Reprinted
[40]
from Additive Manufacturing, 8, S. M. Thompson, L. Bian, powder preparation, the Ni/Ti ratio is an essential factor
N. Shamsaei, et al., An overview of Direct Laser Deposition for in ensuring the required functional properties (SME or
additive manufacturing ; Part I : Transport phenomena, modeling, superelasticity) of the final part. At room temperature,
[43]
and diagnostics, 36–62, Copyright (2015), with permission from parts made of Ti-rich NiTi have a SME , while parts made
Elsevier). of Ni-rich NiTi exhibits superelasticity after annealing or
A B
Figure 3. DED/LENS process. (A) Laser head set up. (B) Powder feeding setup (Lasers in Manufacturing and Materials Processing,
[41]
Effects of Composition and Post Heat Treatment on Shape Memory Characteristics and Mechanical Properties for Laser Direct Deposited
Nitinol, 6, 2019, 41–58, J. Lee, Y. C. Shin. With permission from Springer).
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2 17