Page 31 - IJB-7-2
P. 31
Zhang, et al.
A B
C
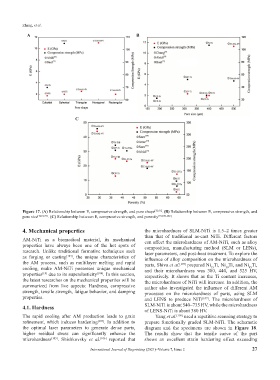
Figure 17. (A) Relationship between E, compressive strength, and pore shape [72,91] . (B) Relationship between E, compressive strength, and
pore size [72,91,93] . (C) Relationship between E, compressive strength, and porosity [91,100-102] .
4. Mechanical properties the microhardness of SLM-NiTi is 1.5–2 times greater
than that of traditional as-cast NiTi. Different factors
AM-NiTi as a biomedical material, its mechanical can affect the microhardness of AM-NiTi, such as alloy
properties have always been one of the hot spots of composition, manufacturing method (SLM or LENs),
research. Unlike traditional formative techniques such laser parameters, and post-heat treatment. To explore the
as forging or casting [103] , the unique characteristics of influence of alloy composition on the microhardness of
the AM process, such as multilayer melting and rapid parts, Shiva et al. [107] prepared Ni Ti, Ni Ti, and Ni Ti,
cooling, make AM-NiTi possesses unique mechanical and their microhardness was 380, 440, and 525 HV,
50
45
55
properties due to its superelasticity [104] . In this section, respectively. It shows that as the Ti content increases,
[19]
the latest researches on the mechanical properties will be the microhardness of NiTi will increase. In addition, the
summarized from five aspects: Hardness, compressive author also investigated the influence of different AM
strength, tensile strength, fatigue behavior, and damping processes on the microhardness of parts, using SLM
properties. and LENS to produce NiTi [107] . The microhardness of
4.1. Hardness SLM-NiTi is about 540–735 HV, while the microhardness
of LENS-NiTi is about 380 HV.
The rapid cooling after AM production leads to grain Yang et al. [108] used a repetitive scanning strategy to
refinement, which induces hardening [105] . In addition to prepare functionally graded SLM-NiTi. The schematic
the optimal laser parameters to generate dense parts, diagram and the specimens are shown in Figure 18.
higher residual stress can significantly enhance the The results show that the tensile curve of the part
microhardness [105] . Shishkovsky et al. [106] reported that shows an excellent strain hardening effect exceeding
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 2 27