Page 146 - IJB-7-3
P. 146
A Dual-Sensitive Hydrogel for 3D Printing
A
B
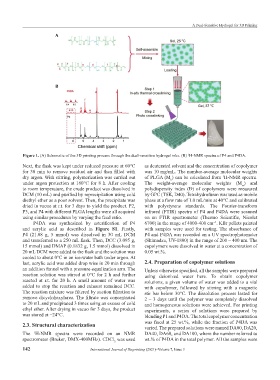
Figure 1. (A) Schematic of the 3D printing process through the dual-sensitive hydrogel inks. (B) H-NMR spectra of P4 and P4DA.
1
Next, the flask was kept under reduced pressure at 60°C as deuterated solvent and the concentration of copolymer
for 30 min to remove residual air and then filled with was 10 mg/mL. The number-average molecular weights
dry argon. With stirring, polymerization was carried out of PLGA (M ) can be calculated from H-NMR spectra.
1
n
under argon protection at 160°C for 8 h. After cooling The weight-average molecular weights (M ) and
w
to room temperature, the crude product was dissolved in polydispersity index (Ð) of copolymers were measured
DCM (10 mL) and purified by reprecipitation using cold by GPC (TSK, D40). Tetrahydrofuran was used as mobile
diethyl ether as a poor solvent. Then, the precipitate was phase at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min at 40°C and calibrated
dried in vacuo at r.t. for 3 days to yield the product. P2, with polystyrene standards. The Fourier-transform
P3, and P4 with different PLGA lengths were all acquired infrared (FTIR) spectra of P4 and P4DA were scanned
using similar procedures by varying the feed ratio. on an FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, Nicolet
P4DA was synthesized by esterification of P4 6700) in the range of 4000-400 cm . KBr pellets painted
−1
and acrylic acid as described in Figure S1. Firstly, with samples were used for testing. The absorbance of
P4 (21.08 g, 5 mmol) was dissolved in 30 mL DCM P4 and P4DA was recorded on a UV spectrophotometer
and transferred to a 250 mL flask. Then, DCC (3.095 g, (Shimadzu, UV-1800) in the range of 200 – 400 nm. The
15 mmol) and DMAP (0.1832 g, 1.5 mmol) dissolved in copolymers were dissolved in water at a concentration of
20 mL DCM were added to the flask and the solution was 0.05 wt.%.
cooled to about 0°C in an ice-water bath under argon. At
last, acrylic acid was added drop wise in 20 min through 2.4. Preparation of copolymer solutions
an addition funnel with a pressure-equalization arm. The Unless otherwise specified, all the samples were prepared
reaction solution was stirred at 0°C for 2 h and further using deionized water here. To obtain copolymer
reacted at r.t. for 20 h. A small amount of water was solutions, a given volume of water was added to a vial
added to stop the reaction and exhaust remained DCC. with copolymer, followed by stirring with a magnetic
The reaction mixture was filtered by suction filtration to stir bar below 30°C. The dissolution process lasted for
remove dicyclohexylurea. The filtrate was concentrated 2 – 3 days until the polymer was completely dissolved
to 20 mL and precipitated 3 times using an excess of cold and homogeneous solutions were achieved. For printing
ethyl ether. After drying in vacuo for 3 days, the product experiments, a series of solutions were prepared by
was stored at −24°C. blending P1 and P4DA. The total copolymer concentration
2.3. Structural characterization was fixed at 25 wt.%, while the fraction of P4DA was
varied. The prepared solutions were named DA00, DA20,
The H-NMR spectra were recorded on an NMR DA40, DA60, and DA100, where the number referred to
1
spectrometer (Bruker, DMX-400MHz). CDCl was used wt.% of P4DA in the total polymer. All the samples were
3
142 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3