Page 120 - IJB-7-4
P. 120
CNC-enhanced Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting
(2.2, 4.4, and 8.8 wt%, respectively) were added to the hydrogels to varying degrees, it is thereby predictable that
hydrogels. Among them, the effect on PCA is the most the mechanical strength of the hydrogels may be similarly
3
remarkable. When the concentration of CNCs reaches 8.8 enhanced by CNC. Therefore, the rheological properties
wt%, the LCGT of PCA increased by about 15°C, showing of the copolymers were investigated. Frequency sweep
3
a notable promotion effect. was conducted (Figure 4). For PCA and PCA , the
2
1
This enhancement effect on phase transition with addition of CNCs significantly improved the modulus of
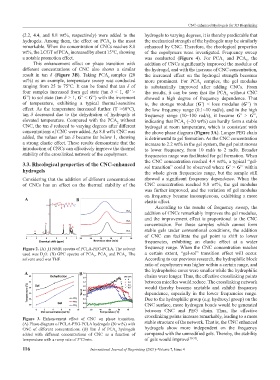
different concentrations of CNC also shows a similar the hydrogel, and with the increase of CNC concentration,
result in tan δ (Figure 3B). Taking PCA samples (20 the increased effect on the hydrogel strength becomes
2
wt%) as an example, temperature sweep was conducted more prominent. For PCA samples, the gel modulus
3
ranging from 25 to 75°C. It can be found that tan δ of is substantially improved after adding CNCs. From
four samples increased from gel state (tan δ < 1, G’ > the results, it can be seen that the PCA without CNC
3
G’’) to sol state (tan δ > 1, G’ < G’’) with the increment showed a high degree of frequency dependence. That
of temperature, exhibiting a typical thermal-sensitive is, the storage modulus (G’) < loss modulus (G’’) in
effect. As the temperature increased further (T >60°C), the low frequency range (0.1~10 rad/s), and in the high
tan δ decreased due to the dehydration of hydrogels at frequency range (10~100 rad/s), it became G’ > G’’,
elevated temperature. Compared with the PCA without indicating that PCA (~20 wt%) can hardly form a stable
2
3
CNC, the tan δ reduced to varying degrees after different hydrogel at room temperature, which is consistent with
concentrations of CNC were added. As 8.8 wt% CNC was the above phase diagram (Figure 3A). Longer PEG chain
added, the values of tan δ became far below 1, showing is detrimental to gel formation. As the CNC concentration
a strong elastic effect. These results demonstrate that the increase to 2.2 wt% in the gel system, the gel point moves
introduction of CNCs can effectively improve the thermal to lower frequency, from 10 rad/s to 2 rad/s. Broader
stability of the crosslinked network of the copolymers. frequencies range was facilitated for gel formation. When
3.3. Rheological properties of the CNC-enhanced the CNC concentration reached 4.4 wt%, a typical “gel-
sol transition” could be observed where G’ > G’’ within
hydrogels the whole given frequencies range, but the sample still
Considering that the addition of different concentrations showed a significant frequency dependence. When the
of CNCs has an effect on the thermal stability of the CNC concentration reached 8.8 wt%, the gel modulus
was further improved, and the variation of gel modulus
on frequency became inconspicuous, exhibiting a more
A B elastic effect.
According to the results of frequency sweep, the
addition of CNCs remarkably improves the gel modulus,
and the improvement effect is proportional to the CNC
concentration. For those samples which cannot form
stable gels under conventional conditions, the addition
of CNC can facilitate the gel point to shift to lower
frequencies, exhibiting an elastic effect at a wider
Figure 2. (A) H NMR spectra of PCLA-PEG-PCLA. The solvent frequency range. When the CNC concentration reaches
1
used was D O. (B) GPC spectra of PCA , PCA and PCA . The a certain extent, “gel-sol” transition effect will occur.
3
2
1
2
solvent used was THF. According to our previous research, the hydrophilic block
ratio of copolymers was higher within a certain range, and
the hydrophobic cores were smaller while the hydrophilic
A B chains were longer. Thus, the effective crosslinking points
between micelles would reduce. The crosslinking network
would thereby become unstable and exhibit frequency
dependence, especially in the lower frequencies range.
Due to the hydrophilic group (e.g. hydroxyl group) on the
CNC surface, more hydrogen bonds would be generated
between CNC and PEG chain. Thus, the effective
crosslinking points increase remarkably, leading to a more
Figure 3. Enhancement effect of CNC on phase transition.
(A) Phase diagram of PCLA-PEG-PCLA hydrogels (20 wt%) with stable structure of the network. That is, the CNC enhanced
CNC of different concentrations. (B) Tan δ of PCA hydrogels hydrogels show more independent on the frequency
2
added with different concentrations of CNC as a function of compared with the unmodified gels. Thereby, the stability
temperature with a ramp rate of 3°C/min. of gels would improve [30-35] .
116 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 4