Page 124 - IJB-7-4
P. 124
CNC-enhanced Hydrogels for 3D Bioprinting
temperature. The enhancement effect was proportional to
CNC concentration within certain range. The printed 3D
construct of CNC-enhanced copolymer formed hydrogels
have strong mechanical properties to maintain the shape
with high resolution and precision. These results proved
that for the amorphous hydrogels, the printability of
materials can be improved by adding rigid nanocrystals
such as CNC. This method provides an effective approach
of enhancing the comprehensive performance of materials
for 3D bioprinting and other additive manufacturing
technologies.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Key
R&D Program of China (2017YFC1103400)..
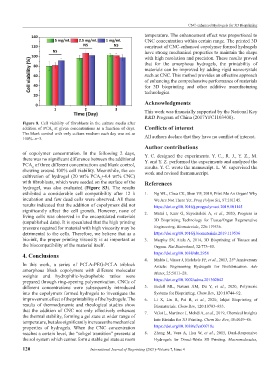
Figure 8. Cell viability of fibroblasts in the culture media after
addition of PCA at given concentrations as a function of days. Conflicts of interest
2
The blank control with only culture medium each day was set as
100%. n=3. All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author contributions
of copolymer concentration. In the following 2 days, Y. C. designed the experiments. Y. C., R. J., Y. Z., M.
there was no significant difference between the additional Y. and Y. Z. performed the experiments and analyzed the
PCA of three different concentrations and blank control, results. Y. C. wrote the manuscript. L. W. supervised the
2
showing around 100% cell viability. Meanwhile, the co- work and revised themanuscript.
cultivation of hydrogel (20 wt% PCA +4.4 wt% CNC)
2
with fibroblasts, which were seeded on the surface of the References
hydrogel, was also evaluated (Figure S3). The results
exhibited a considerable cell compatibility after 12 h 1. Ng WL, Chua CK, Shen YF, 2019, Print Me An Organ! Why
incubation and few dead cells were observed. All these We Are Not There Yet. Prog Polym Sci, 97:101145.
results indicated that the addition of copolymers did not https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2019.101145
significantly affect the cell growth. However, none of 2. Matai I, Kaur G, Seyedsalehi A, et al., 2020, Progress in
living cells was observed in the encapsulated materials
(unpublished data). It is speculated that the high printing 3D Bioprinting Technology for Tissue/Organ Regenerative
pressure required for material with high viscosity may be Engineering. Biomaterials, 226:119536.
detrimental to the cells. Therefore, we believe that as a https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119536
bio-ink, the proper printing viscosity is as important as 3. Murphy SV, Atala A, 2014, 3D Bioprinting of Tissues and
the biocompatibility of the material itself. Organs. Nat Biotechnol, 32:773–85.
4. Conclusions https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2958
4. Malda J, Visser J, Melchels FP, et al., 2013, 25 Anniversary
th
In this work, a series of PCLA-PEG-PCLA triblock Article: Engineering Hydrogels for Biofabrication. Adv
amorphous block copolymers with different molecular Mater, 25:5011–28.
weights and hydrophilic-hydrophobic ratios were
prepared through ring-opening polymerization. CNCs of https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302042
different concentrations were subsequently introduced 5. Bedell ML, Navara AM, Du Y, et al., 2020, Polymeric
into the copolymers formed hydrogels to investigate the Systems for Bioprinting. Chem Rev, 120:10744–92.
improvement effect of the printability of the hydrogels. The 6. Li X, Liu B, Pei B, et al., 2020, Inkjet Bioprinting of
results of thermodynamic and rheological studies show Biomaterials. Chem Rev, 120:10793–833.
that the addition of CNC not only effectively enhances 7. Valot L, Martinez J, Mehdi A, et al., 2019, Chemical Insights
the thermal stability, forming a gel state at wider range of Into Bioinks for 3D Printing. Chem Soc Rev, 48:4049–86.
temperature, but also significantly increases the mechanical
properties of hydrogels. When the CNC concentration https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00718c
reaches a certain level, the “sol-gel transition” presents at 8. Zhang M, Vora A, Han W, et al., 2015, Dual-Responsive
the sol system which cannot form a stable gel state at room Hydrogels for Direct-Write 3D Printing. Macromolecules,
120 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 4