Page 121 - IJB-7-4
P. 121
Cui, et al.
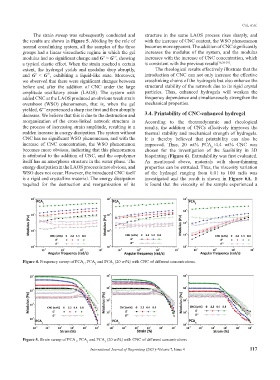
The strain sweep was subsequently conducted and structure in the same LAOS process rises sharply, and
the results are shown in Figure 5. Abiding by the rule of with the increase of CNC content, the WSO phenomenon
normal crosslinking system, all the samples of the three becomes more apparent. The addition of CNC significantly
groups had a linear viscoelastic regime in which the gel increases the modulus of the system, and the modulus
modulus had no significant change and G’ > G’’, showing increases with the increase of CNC concentration, which
a typical elastic effect. When the strain reached a certain is consistent with the previous results [16,36-39] .
extent, the hydrogel yields and modulus drop abruptly, The rheological results effectively illustrate that the
and G’ < G’’, exhibiting a liquid-like state. Moreover, introduction of CNC can not only increase the effective
we observed that there were significant changes between crosslinking chains of the hydrogels but also enhance the
before and after the addition of CNC under the large structural stability of the network due to its rigid crystal
amplitude oscillatory strain (LAOS). The system with particles. Thus, enhanced hydrogels will weaken the
added CNC at the LAOS produced an obvious weak strain frequency dependence and simultaneously strengthen the
overshoot (WSO) phenomenon, that is, when the gel mechanical properties.
yielded, G’’ experienced a sharp rise first and then abruptly
decrease. We believe that this is due to the destruction and 3.4. Printability of CNC-enhanced hydrogel
reorganization of the cross-linked network structure in According to the thermodynamic and rheological
the process of increasing strain amplitude, resulting in a results, the addition of CNCs effectively improves the
sudden increase in energy dissipation. The system without thermal stability and mechanical strength of hydrogels.
CNC has no significant WSO phenomenon, and with the It is thereby believed that printability can also be
increase of CNC concentration, the WSO phenomenon improved. Thus, 20 wt% PCA +4.4 wt% CNC was
2
becomes more obvious, indicating that this phenomenon chosen for the investigation of the feasibility in 3D
is attributed to the addition of CNC, and the copolymer bioprinting (Figure 6). Extrudability was first evaluated.
itself has an amorphous structure in the water phase. The As mentioned above, materials with shear-thinning
energy dissipation in the LAOS process is not obvious, and properties can be extruded. Thus, the viscosity variation
WSO does not occur. However, the introduced CNC itself of the hydrogel ranging from 0.01 to 100 rad/s was
is a rigid and crystalline material. The energy dissipation investigated and the result is shown in Figure 6A. It
required for the destruction and reorganization of its is found that the viscosity of the sample experienced a
Figure 4. Frequency sweep of PCA , PCA and PCA (20 wt%) with CNC of different concentrations.
2
3
1
Figure 5. Strain sweep of PCA , PCA and PCA (20 wt%) with CNC of different concentrations
1
2
3
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 4 117