Page 170 - IJB-8-1
P. 170
Optimization of 3D Printing Parameters of PLA/HA Bone Plates
A B B CC
D E F F G G
H I J J K K
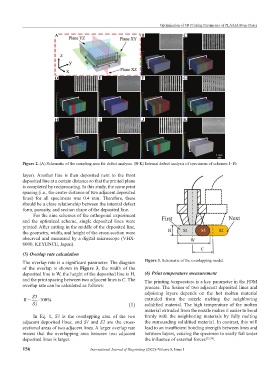
Figure 2. (A) Schematic of the sampling area for defect analysis. (B-K) Internal defect analysis of specimens of schemes 1-10.
layer). Another line is then deposited next to the front
deposited line at a certain distance so that the printed plane
is completed by reciprocating. In this study, the same print
spacing (i.e., the center distance of two adjacent deposited
lines) for all specimens was 0.4 mm. Therefore, there
should be a close relationship between the internal defect
form, porosity, and section shape of the deposited line.
For the nine schemes of the orthogonal experiment
and the optimized scheme, single deposited lines were
printed. After cutting in the middle of the deposited line,
the geometry, width, and height of the cross-section were
observed and measured by a digital microscope (VHX-
6000, KEYENCE, Japan).
(5) Overlap rate calculation
The overlap rate is a significant parameter. The diagram Figure 3. Schematic of the overlapping model.
of the overlap is shown in Figure 3, the width of the
deposited line is W, the height of the deposited line is H, (6) Print temperature measurement
and the print spacing between two adjacent lines is C. The The printing temperature is a key parameter in the FDM
overlap rate can be calculated as follows: process. The fusion of two adjacent deposited lines and
adjoining layers depends on the hot molten material
S 3
R = ⋅ 100% extruded from the nozzle melting the neighboring
1 S (1) solidified material. The high temperature of the molten
material extruded from the nozzle makes it easier to bond
In Eq. 1, S3 is the overlapping area of the two firmly with the neighboring materials by fully melting
adjacent deposited lines, and S1 and S2 are the cross- the surrounding solidified material. In contrast, this will
sectional areas of two adjacent lines. A larger overlap rate lead to an insufficient bonding strength between lines and
means that the overlapping area between two adjacent between layers, causing the specimen to easily fail under
deposited lines is larger. the influence of external forces [35,36] .
156 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 1