Page 75 - IJB-8-2
P. 75
Zhang, et al.
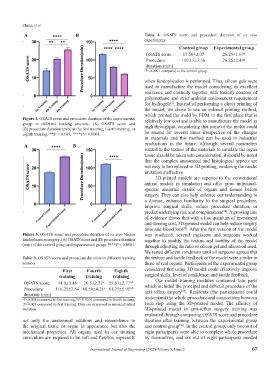
A B Table 4. OSATS score and procedure duration of ex vivo
experiments
Control group Experimental group
OSATS score 17.50±2.07 26.25±1.67 a
Procedure 110.13±3.36 76.25±2.49 a
duration (min)
a P<0.0001 compared to the control group.
when fundoplication is performed. Thus, silicon gels were
used to manufacture the model considering its excellent
resilience and elasticity together with toxicity concern of
polyurethane and strict ambient environment requirement
for hydrogels . Instead of performing a direct printing of
[5]
the model, we chose to use an indirect printing method,
which printed the mold by FDM in the first place that is
Figure 4. OSATS score and procedure duration of the experimental relatively low cost and is able to manufacture the model in
group in different training sessions. (A) OSATS score and
(B) procedure duration (min) at the first training, fourth training, or high throughput, considering that some of the molds could
eighth training. **P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0001. be reused for several times irrespective of the changes
in materials and this method can be used in industrial
A B productions in the future. Although several parameters
related to the texture of the materials to simulate the organ
tissue should be taken into consideration, it should be noted
that the complex anatomical and histological aspects are
not easy to be replaced in 3D printing, rendering the model
imitation ineffective.
3D-printed models are superior to the conventional
animal models in simulation and offer more individual-
specific anatomic details of organs and tissues before
surgery. They can also help enhance our understanding to
a disease, enhance familiarity to the surgical procedure,
improve surgical skills, reduce procedure duration, or
predict underlying risk and complications . A growing line
[20]
of evidence shows that with a low quantum of investment
and running cost, 3D-printed model can help reduce surgery
time and blood loss . After the first version of the model
[29]
Figure 5. OSATS score and procedure duration of ex vivo Nissen was produced, several engineers and surgeons worked
fundoplication surgery. (A) OSATS score and (B) procedure duration together to modify the texture and tactility of the model
(min) of the control group and experimental group. ****P < 0.0001. through adjusting the ratio of silicon gel and silicon oil used.
We tested different conditions until all surgeons agreed that
Table 3. OSATS score and procedure duration in different training the texture and tactile feedback of the model were similar to
session those of real organs. Participants of the experimental group
First Fourth Eighth considered that using 3D model could effectively improve
training training training surgical skills, level of confidence, and tactile feedback.
OSATS score 14.0±3.46 20.5±2.27 c 25.63±2.77 a,b Our model training modules contained four parts
Procedure 116.25±3.54 80.50±4.21 c 61.25±5.95 a,b which included the principal and difficult procedure of the
anti-reflux surgery . Residents (the participants) could
[25]
duration (min)
b
a P<0.005 compared to first training, P<0.0001 compared to fourth training, understand the whole procedure and connections between
c P<0.005 compared to first training. Data are expressed as mean±standard each step using the 3D-printed model. The efficacy of
variation 3D-printed model in anti-reflux surgery training was
evaluated through comparing OSATS score and procedure
not only the anatomical relations and resemblance to duration after training between the experimental group
the original tissue or organ in appearance but also the and control group . In the control group, only two out of
[30]
mechanical properties. All organs used in our training eight participants were able to complete whole procedure
curriculum are required to be soft and flexible, especially by themselves, and six out of eight participants needed
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 67