Page 218 - IJB-8-3
P. 218
Stakeholder Perspectives on the Current and Future of Additive Manufacturing in Healthcare
finish (3.6 ± 1.7) or mechanical behavior (4.7 ± 0.8) increased confidence in their adoption [41-43] . Nevertheless,
and biological compatibility (3.7 ± 2.0) are the highest certification is still considered one of the main constraints
and lowest priorities for academia and manufacturing, of modern AM [29,40,44] , which may explain the required
respectively. As expected, biological compatibility features for success mentioned in this survey.
overshadows all other requirements from a medical
perspective (5.0 ± 0.0), with repeatability ranked lowest 3.4. Advantages, limitations, and future
(3.8 ± 1.6). perspectives of AM
From the point of view of academic, design and To expand our understanding on the vision of AM as
manufacturing experts, simplicity, repeatability, part seen by different specialists, specific details were asked
quality, and flexibility are some of the most desirable on the main advantages and disadvantages in healthcare
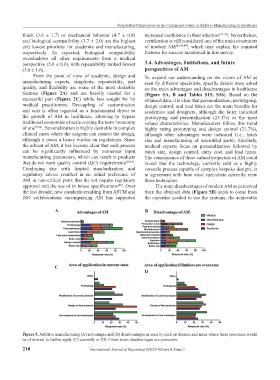
features (Figure 2A) and are heavily needed for a (Figure 5A, B and Tables S15, S16). Based on the
successful part (Figure 2C) while less sought for by obtained data, it is clear that personalization, prototyping,
medical practitioners. Decoupling of customization design control, and lead times are the main benefits for
and cost is often regarded as a fundamental driver to academics and designers, although the latter indicated
the growth of AM in healthcare, allowing to bypass prototyping and personalization (23.1%) as the most
traditional economies of scale coining the term “economy valued characteristics. Manufacturers follow this trend
of one” . Personalization is highly desirable in complex highly rating prototyping and design control (21.7%),
[38]
clinical cases where the surgeon can control the design, although other advantages were indicated (i.e., batch
although it poses a heavy burden on regulations. Since size and manufacturing of assembled parts). Similarly,
the advent of AM, it has become clear that each process medical experts focus on personalization followed by
can be significantly influenced by numerous input batch size, design control, entry cost, and lead times.
manufacturing parameters, which can result in products The consequence of these valued properties of AM could
that do not meet quality control (QC) requirements [29,39] . reveal that the technology, currently sold as a highly
Combining this with limited standardization and versatile process capable of complex bespoke designs, is
regulatory advice resulted in an initial preference of in agreement with how most specialists currently view
AM in non-critical parts that do not require regulatory these techniques.
approval and the use of in house specifications . Over The main disadvantages of modern AM as perceived
[40]
the last decade, new standards resulting from ASTM and from the obtained data (Figure 5B) seem to come from
ISO collaborations encompassing AM has supported the expertise needed to use the systems, the achievable
A B
C
D
Figure 5. Additive manufacturing (A) advantages and (B) disadvantages as seen by each profession and areas where these processes would
be of interest to further apply (C) currently or (D) if their main disadvantages are overcome.
210 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3