Page 232 - IJB-8-3
P. 232
Multifunctional 3D Printed Composite Hydrogel
A B C
D E F
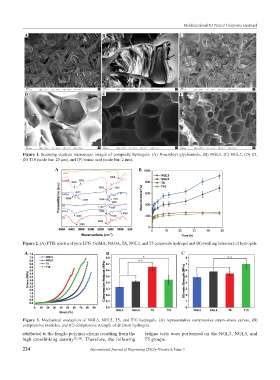
Figure 1. Scanning electron microscope images of composite hydrogels: (A) N-acryloyl glycinamide, (B) NGL3, (C) NGL5, (D) T5,
(E) T10 (scale bar: 20 µm), and (F) tannic acid (scale bar: 2 µm).
A B
Figure 2. (A) FTIR spectra of pure LPN, GelMA, NAGA, TA, NGL3, and T5 composite hydrogel and (B) swelling behaviors of hydrogels.
A B C
Figure 3. Mechanical evaluation of NGL3, NGL5, T5, and T10 hydrogels. (A) representative compressive strain–stress curves, (B)
compressive modulus, and (C) compressive strength of different hydrogels.
attributed to the fragile polymer chains resulting from the fatigue tests were performed on the NGL3, NGL5, and
high crosslinking density [35,36] . Therefore, the following T5 groups.
224 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3