Page 234 - IJB-8-3
P. 234
Multifunctional 3D Printed Composite Hydrogel
The increase in the adhesion strength was attributed solutions were demonstrated in blue, purple, and blue-
to the borate ester formed by borax and polyphenols. violet, respectively. When the T5 hydrogel was added to
Consequently, when tested with various substrates, the the solution, the absorbance sharply decreased, and all the
T5 hydrogel exhibited universal adhesive properties and original colors in the solution changed to light yellow.
excellent adhesion to different underwater substrates, Because the PTIO method measures the transfer capacity
indicating its universal potential as an adhesive material of oxygen free radicals , it was confirmed that the
[38]
for medical applications. antioxidant capacity of the hydrogel was concentration-
dependent.
3.4. Antioxidant property of hydrogels As shown in Figure 6F, a higher TA content led to
The ABTS, DPPH, and PTIO methods were used to a greater clearance rate for the sample. However, when
evaluate the antioxidative efficiency of T5 hydrogel. As the TA content exceeded 10%, the clearance rate was no
shown in Figure 6A-C, the ABTS, DPPH, and PTIO significant difference between the T10 and TA powder
A B
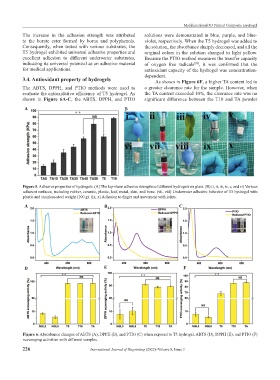
Figure 5. Adhesive properties of hydrogels. (A) The lap-shear adhesive strengths of different hydrogels on glass. (B) (i, ii, iii, iv, v, and vi) Various
adherent surfaces, including rubber, ceramic, plastic, leaf, metal, skin, and bone. (vii, viii) Underwater adhesive behavior of T5 hydrogel with
plastic and stainless-steel weight (100 g). (ix, x) Adhesion to finger and movement with joints.
A B C
D E F
Figure 6. Absorbance changes of ABTS (A), DPPH (B), and PTIO (C) when exposed to T5 hydrogel. ABTS (D), DPPH (E), and PTIO (F)
scavenging activities with different samples.
226 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3