Page 311 - IJB-8-4
P. 311
Gu, et al.
and inhibits VEGFR binding, thereby preventing tumor which is another monoclonal antibody that binds to
[46]
blood vessels from being maintained or developing. Three VEGFR-2 and blocks the activation of the receptor ;
concentrations of bevacizumab (MedChemExpress, US) aflibercept, which is a recombinant fusion protein that
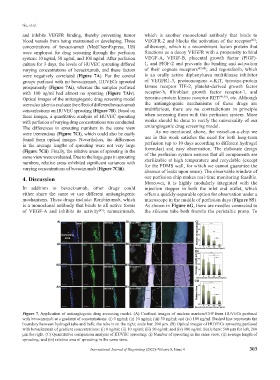
were employed for drug screening through the perfusion functions as a decoy VEGFR with a propensity to bind
system: 10 ng/ml, 50 ng/ml, and 100 ng/ml. After perfusion VEGF-A, VEGF-B, placental growth factor (PlGF)-
culture for 3 days, the levels of HUVEC sprouting differed 1, and PlGF-2 and prevents the binding and activation
varying concentrations of bevacizumab, and these factors of their cognate receptors [47,48] ; and regorafenib, which
were negatively correlated (Figure 7A). For the control is an orally active diphenylurea multikinase inhibitor
groups perfused with no bevacizumab, HUVECs sprouted of VEGFR1-3, protooncogene c-KIT, tyrosine-protein
prosperously (Figure 7Ai), whereas the samples perfused kinase receptor TIE-2, platelet-derived growth factor
with 100 ng/ml had almost no spouting (Figure 7Aiv). receptor-b, fibroblast growth factor receptor-1, and
Optical images of the antiangiogenic drug screening model tyrosine-protein kinase receptor RET [49,50] , etc. Although
were also taken to evaluate the effect of different bevacizumab the antiangiogenic mechanisms of these drugs are
concentrations on HUVEC sprouting (Figure 7B). Based on multifarious, there are no contradictions in principle
these images, a quantitative analysis of HUVEC sprouting when screening them with this perfusion system. More
with perfusion of varying drug concentrations was conducted. works should be done to verify the universality of our
The differences in sprouting numbers in the same view antiangiogenic drug screening model.
were tremendous (Figure 7Ci), which could also be easily As we mentioned above, the vessel-on-a-chip we
found from optical images. Nevertheless, the differences use in this work satisfies the need for both long-term
in the average lengths of sprouting were not very large perfusion (up to 10 days according to different hydrogel
(Figure 7Cii). Finally, the relative areas of sprouting in the formulas) and easy observation. The elaborate design
same view were evaluated. Due to the large gaps in sprouting of the perfusion system ensures that all components are
numbers, relative areas exhibited significant variances with sterilizable at high temperature and recyclable (except
varying concentrations of bevacizumab (Figure 7Ciii). for the PDMS wall, for which we cannot guarantee the
absence of leaks upon reuse). The observable window of
4. Discussion our perfusion chip makes real-time monitoring feasible.
Moreover, it is highly modularly integrated with the
In addition to bevacizumab, other drugs could injection stopper in both the inlet and outlet, which
either share the same or use different antiangiogenic offers a quickly-separable option for observation under a
mechanisms. These drugs include: Ranibizumab, which microscope in the middle of perfusion days (Figure S5).
is a monoclonal antibody that binds to all active forms As shown in Figure 6G, there are needles connected to
of VEGF-A and inhibits its activity ; ramucirumab, the silicone tube both from/to the peristaltic pump. To
[45]
Figure 7. Application of antiangiogenic drug screening model. (A) Confocal images of nucleus markers/GFP from HUVECs perfused
with bevacizumab at a gradient of concentrations: (i) 0 ng/ml; (ii) 10 ng/ml; (iii) 50 ng/ml; and (iv) 100 ng/ml. Dashed line represents the
boundary between hydrogel tube and bulk; the tube is on the right; scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Optical images of HUVECs sprouting perfused
with bevacizumab of gradient concentrations: (i) 0 ng/ml; (ii) 10 ng/ml; (iii) 50 ng/ml; and (iv) 100 ng/ml. Scale bars: 500 μm for left, 200
μm for right. (C) Quantitative comparison analysis of HUVEC sprouting: (i) Number of sprouting in the same view; (ii) average length of
sprouting; and (iii) relative area of sprouting in the same view.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 303