Page 306 - IJB-8-4
P. 306
Vessel-on-a-Chip for Antiangiogenic Drug Screening
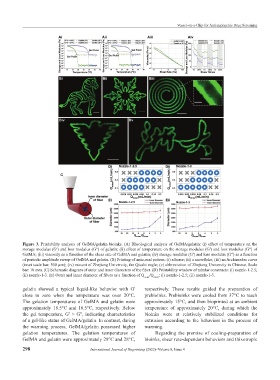
Figure 3. Printability analysis of GelMA/gelatin bioinks. (A) Rheological analysis of GelMA/gelatin: (i) effect of temperature on the
storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of gelatin; (ii) effect of temperature on the storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of
GelMA; (iii) viscosity as a function of the shear rate of GelMA and gelatin; (iv) storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) as a function
of periodic amplitude sweep of GelMA and gelatin. (B) Printing of unicursal pattern: (i) a horse; (ii) a snowflake; (iii) an Archimedes curve
(inset scale bar: 500 μm); (iv) mascot of Zhejiang University, the Qiushi eagle; (v) abbreviation of Zhejiang University in Chinese. Scale
bar: 10 mm. (C) Schematic diagram of outer and inner diameters of the fiber. (D) Printability window of tubular constructs: (i) nozzle-1-2.5;
(ii) nozzle-1-3. (E) Outer and inner diameter of fibers as a function of Q outer /Q inner : (i) nozzle-1-2.5; (ii) nozzle-1-3.
gelatin showed a typical liquid-like behavior with G′ respectively. These results guided the preparation of
close to zero when the temperature was over 20°C. prebioinks. Prebioinks were cooled from 37°C to reach
The gelation temperatures of GelMA and gelatin were approximately 15°C, and then bioprinted at an ambient
approximately 18.5°C and 16.5°C, respectively. Below temperature of approximately 20°C, during which the
the gel temperature, G′ > G″, indicating characteristics bioinks were at relatively stabilized conditions for
of a gel-like status of GelMA/gelatin. In contrast, during extrusion according to the behaviors in the process of
the warming process, GelMA/gelatin possessed higher warming.
gelation temperatures. The gelation temperatures of Regarding the premise of cooling-preparation of
GelMA and gelatin were approximately 29°C and 28°C, bioinks, shear rate-dependent behaviors and thixotropic
298 International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4