Page 224 - IJB-9-1
P. 224
International Journal of Bioprinting Cellulose-based bio-inks for bone and cartilage TE
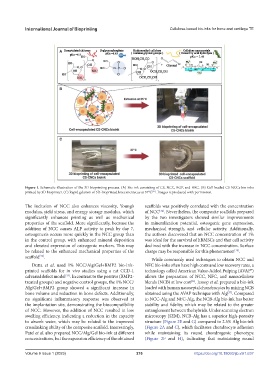
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the 3D bioprinting process. (A) Bio-ink consisting of CS, NCC, BGP, and HEC. (B) Cell-loaded CS-NCCs bio-inks
printed by 3D bioprinter. (C) Rapid gelation of 3D-bioprinted knee meniscus at 37°C . Images reproduced with permission.
[31]
The inclusion of NCC also enhances viscosity, Young’s scaffolds was positively correlated with the concentration
modulus, yield stress, and energy storage modulus, which of NCC . Nevertheless, the composite scaffolds prepared
[34]
significantly enhances printing as well as mechanical by the two investigators showed similar improvements
properties of the scaffold. More significantly, because the in mineralization potential, osteogenic gene expression,
addition of NCC causes ALP activity to peak by day 7, mechanical strength, and cellular activity. Additionally,
osteogenesis occurs more quickly in the NCC group than the authors discovered that an NCC concentration of 1%
in the control group, with enhanced mineral deposition was ideal for the survival of hBMSCs and that cell activity
and elevated expression of osteogenic markers. This may declined with the increase in NCC concentration. Surface
be related to the enhanced mechanical properties of the charge may be responsible for this phenomenon .
[35]
scaffold .
[32]
While commonly used techniques to obtain NCC and
Dutta et al. used 1% NCC/Alg/Gel+BMP2 bio-ink- NFC bio-inks often have high costs and low recovery rates, a
printed scaffolds for in vivo studies using a rat CCD-1 technology called American Value-Added Pulping (AVAP®)
calvarial defect model . In contrast to the positive (BMP2- allows the preparation of NCC, NFC, and nanocellulose
[33]
treated groups) and negative control groups, the 1% NCC/ blends (NCB) at low cost . Jessop et al. prepared a bio-ink
[36]
Alg/Gel+BMP2 group showed a significant increase in loaded with human nasoseptal chondrocytes by mixing NCB
bone volume and reduction in bone defects. Additionally, obtained using the AVAP technique with Alg . Compared
[37]
no significant inflammatory response was observed at to NCC-Alg and NFC-Alg, the NCB-Alg bio-ink has better
the implantation site, demonstrating the biocompatibility stability and fidelity, which may be related to the greater
of NCC. However, the addition of NCC resulted in low entanglement between the hybrids. Under scanning electron
swelling efficiency, indicating a reduction in the capacity microscopy (SEM), NCB-Alg has a superior high-porosity
to absorb water, which may be related to the improved structure (Figure 2E and G) compared to 2.5% Alg bio-ink
crosslinking ability of the composite scaffold. Interestingly, (Figure 2A and C), which facilitates chondrocyte adhesion
Patel et al. also prepared NCC/Alg/Gel bio-ink at different while maintaining its round chondrogenic phenotype
concentrations, but the expansion efficiency of the obtained (Figure 2F and H), indicating that maintaining round
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023)
V 216 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.637