Page 242 - IJB-9-1
P. 242
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing of smart constructs for precise medicine
A B C
D
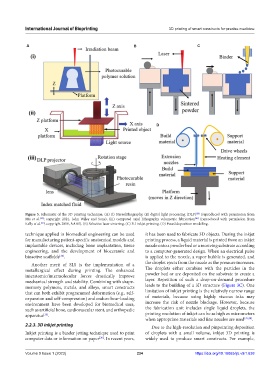
Figure 3. Schematic of the 3D printing technique. (A) (i) Stereolithography, (ii) digital light processing (DLP) (reproduced with permission from
[25]
Mu et al. ; copyright 2021, John Wiley and Sons), (iii) computed axial lithography volumetric fabrication (reproduced with permission from
[25]
[26]
Kelly et al. ; copyright 2019, AAAS). (B) Selective laser sintering. (C) 3D inkjet printing. (D) Fused deposition modeling.
[26]
technique applied in biomedical engineering can be used it has been used to fabricate 3D objects. During the inkjet
for manufacturing patient-specific anatomical models and printing process, a liquid material is printed from an inkjet
implantable devices, including bone implantation, tissue nozzle onto a powder bed or a receiving substrate according
engineering, and the development of bioceramic and to a computer-generated design. When an electrical pulse
bioactive scaffolds . is applied to the nozzle, a vapor bubble is generated, and
[34]
Another merit of SLS is the implementation of a the droplet ejects from the nozzle as the pressure increases.
metallurgical effect during printing. The enhanced The droplets either combine with the particles in the
interatomic/intermolecular forces drastically improve powder bed or are deposited on the substrate to create a
mechanical strength and stability. Combining with shape- layer. Repetition of such a drop-on-demand procedure
memory polymers, metals, and alloys, smart constructs leads to the building of a 3D structure (Figure 3C). One
that can both exhibit programmed deformation (e.g., self- limitation of inkjet printing is the relatively narrow range
expansion and self-compression) and endure bear-loading of materials, because using highly viscous inks may
environment have been developed for biomedical uses, increase the risk of nozzle blockage. However, because
such as artificial bone, cardiovascular stent, and orthopedic the fabrication unit includes single liquid droplets, the
apparatus . printing resolution of inkjet can be as high as micrometers
[35]
when appropriate materials and fine nozzles are used [37,38] .
2.2.3. 3D inkjet printing Due to the high-resolution and pinpointing deposition
Inkjet printing is a binder jetting technique used to print of droplets with a small volume, inkjet 3D printing is
computer data or information on paper . In recent years, widely used to produce smart constructs. For example,
[36]
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 234 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.638