Page 156 - IJB-9-2
P. 156
International Journal of Bioprinting Enhanced osteogenesis in gelatin releasing bioink
to the larger amount of gelatin entrapped in the hydrogel. The amount of gelatin that remained in the hydrogel
However, there were no significant differences in the disks was also examined at the same time points. It was
compressive modulus of either during the immersion. From found that even when gelatin was released, traces still
the observed changes in the compressive modulus during remained within the hydrogel disks, as shown in Figure 4b.
the entire experiment, the hydrogels could be divided into The results show that when a relatively larger amount
two groups based on their mechanical property: those of gelatin was loaded into the hydrogel (i.e., 7:3 and 5:5
with lesser trapped gelatin (10:0 and 9:1 MA-alginate/ MA-alginate/gelatin), the amount of released gelatin was
gelatin) and those with more trapped gelatin (7:3 and higher than the amount of remaining gelatin. Therefore, it
5:5 MA-alginate/gelatin). The entrapped gelatin was in a is possible that such hydrogels have positive effects on cells
liquid phase; therefore, it would not have contributed to external to and embedded within the hydrogel.
crosslinking or the mechanical property of the hydrogel.
This indicates that these amounts of uncrosslinked gelatin, 3.3. Effect of released gelatin on external cells
which were entrapped, could affect mechanical property As shown in Figure 4a, the higher amount of entrapped
directly because groups with more entrapped gelatin gelatin, the more releasing of uncrosslinked gelatin was
showed lower compressive moduli.
showed gradually. Owing to this, the effects of released
3.2. Release of gelatin from the hydrogel disks gelatin on external cells were investigated.
As mentioned above, the gelatin-containing alginate- To verify the effect of released gelatin on external cells,
based bioinks were developed for higher printability by samples of each hydrogel disk type were added to the top
improving rheological properties through the property of transwells and cultured. Osteoblasts (2 × 10 cells/mL)
4
of gelatin. However, in this study, we used uncrosslinked were cultured in osteogenic differentiation media at the
gelatin in the design for enhancing cell activity. Therefore, bottom of the wells for 7 days. The cell activity results
the releasing profile of gelatin and remaining phenomenon of the external cells are shown in Figure 5. After 4 days
of gelatin in hydrogel after releasing were investigated. of culturing, the cells exposed to the gelatin-containing
The release of gelatin from the different hydrogel disks hydrogels showed higher DNA quantities than those
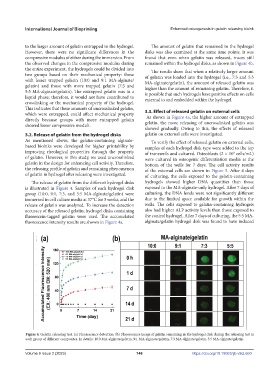
is illustrated in Figure 4. Samples of each hydrogel disk exposed to the MA-alginate-only hydrogel. After 7 days of
group (10:0, 9:1, 7:3, and 5:5 MA-alginate/gelatin) were culturing, the DNA levels were not significantly different
immersed in cell culture media at 37°C for 3 weeks, and the due to the limited space available for growth within the
release of gelatin was analyzed. To increase the detection wells. The cells exposed to gelatin-containing hydrogels
accuracy of the released gelatin, hydrogel disks containing also had higher ALP activity levels than those exposed to
fluorescein-tagged gelatin were used. The accumulated the control hydrogel. After 7 days of culturing, the 5:5 MA-
fluorescence intensity results are shown in Figure 4a. alginate/gelatin hydrogel disk was found to have induced
Figure 4. Gelatin releasing test. (a) Fluorescence detection. (b) Fluorescence image of gelatin remaining in the hydrogel disk during the releasing test in
each group of different composites. In details: 10:0 MA-alginate/gelatin, 9:1 MA-alginate/gelatin, 7:3 MA-alginate/gelatin, 5:5 MA-alginate/gelatin.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 148 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.660