Page 289 - IJB-9-2
P. 289
International Journal of Bioprinting Methodology of hydrogel printability
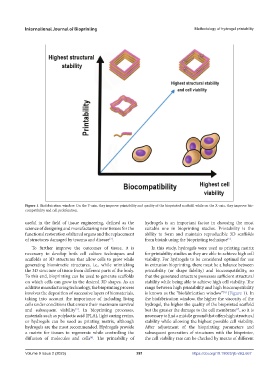
Figure 1. Biofabrication window. On the Y-axis, they improve printability and quality of the bioprinted scaffold, while on the X-axis, they improve bio-
compatibility and cell proliferation.
useful in the field of tissue engineering, defined as the hydrogels is an important factor in choosing the most
science of designing and manufacturing new tissues for the suitable one in bioprinting studies. Printability is the
functional restoration of altered organs and the replacement ability to form and maintain reproducible 3D scaffolds
[5]
[2]
of structures damaged by trauma and disease . from bioink using the bioprinting technique .
To further improve the outcomes of tissue, it is In this study, hydrogels were used as printing matrix
necessary to develop both cell culture techniques and for printability studies as they are able to achieve high cell
scaffolds or 3D structures that allow cells to grow while viability. For hydrogels to be considered optimal for use
generating biomimetic structures, i.e., while mimicking in extrusion bioprinting, there must be a balance between
the 3D structure of tissue from different parts of the body. printability (or shape fidelity) and biocompatibility, so
To this end, bioprinting can be used to generate scaffolds that the generated structure possesses sufficient structural
on which cells can grow in the desired 3D shapes. As an stability while being able to achieve high cell viability. The
additive manufacturing technology, the bioprinting process range between high printability and high biocompatibility
involves the deposition of successive layers of biomaterials, is known as the “biofabrication window” (Figure 1). In
[6]
taking into account the importance of including living the biofabrication window, the higher the viscosity of the
cells under conditions that ensure their maximum survival hydrogel, the higher the quality of the bioprinted scaffold
and subsequent viability . In bioprinting processes, but the greater the damage to the cell membrane , so it is
[3]
[7]
materials such as polylactic acid (PLA), light curing resins, necessary to find a middle ground that offers high structural
or hydrogels can be used as printing matrix, although stability while allowing the highest possible cell viability.
hydrogels are the most recommended. Hydrogels provide After adjustment of the bioprinting parameters and
a matrix for tissues to regenerate while controlling the subsequent generation of structures with the bioprinter,
diffusion of molecules and cells . The printability of the cell viability rate can be checked by means of different
[4]
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 281 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.667