Page 293 - IJB-9-2
P. 293
International Journal of Bioprinting Methodology of hydrogel printability
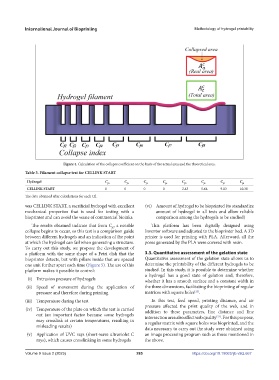
Figure 4. Calculation of the collapse coefficient on the basis of the actual area and the theoretical area.
Table 3. Filament collapse test for CELLINK START
Hydrogel C f1 C f2 C f3 C f4 C f5 C f6 C f7 C f8
CELLINK START 0 0 0 0 2.43 5.64 9.83 10.30
The data obtained after calculations for each Cf.
was CELLINK START, a sacrificial hydrogel with excellent (vi) Amount of hydrogel to be bioprinted (to standardize
mechanical properties that is used for testing with a amount of hydrogel in all tests and allow reliable
bioprinter and can avoid the waste of commercial bioinks. comparison among the hydrogels to be studied)
The results obtained indicate that from C , a notable This platform has been digitally designed using
f5
collapse begins to occur, so this test is a comparison guide Inventor software and adjusted to the bioprinter bed. A 3D
between different hydrogels and an indication of the point printer is used for printing with PLA. Afterward, all the
at which the hydrogel can fail when generating a structure. pores generated by the PLA were covered with resin.
To carry out this study, we propose the development of
a platform with the same shape of a Petri dish that the 3.3. Quantitative assessment of the gelation state
bioprinter detects, but with pillars inside that are spaced Quantitative assessment of the gelation state allows us to
one unit further apart each time (Figure 5). The use of this determine the printability of the different hydrogels to be
platform makes it possible to control: studied. In this study, it is possible to determine whether
a hydrogel has a good state of gelation and, therefore,
(i) Extrusion pressure of hydrogels whether it has a smooth surface and a constant width in
(ii) Speed of movement during the application of the three dimensions, facilitating the bioprinting of regular
[22]
pressure and therefore during printing matrices with square holes .
(iii) Temperature during the test In this test, feed speed, printing distance, and air
pressure affected the print quality of the web, and in
(iv) Temperature of the plate on which the test is carried addition to these parameters, line distance and line
out (an important factor because some hydrogels intersection area also affect web quality . For this purpose,
[23]
may crosslink at certain temperatures, resulting in a regular matrix with square holes was bioprinted, and the
misleading results)
data necessary to carry out the study were obtained using
(v) Application of UVC rays (short-wave ultraviolet C an image processing program such as those mentioned in
rays), which causes crosslinking in some hydrogels the above.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 285 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.667