Page 320 - IJB-9-2
P. 320
International Journal of Bioprinting Flexible 3D printing in cardiovascular medicine
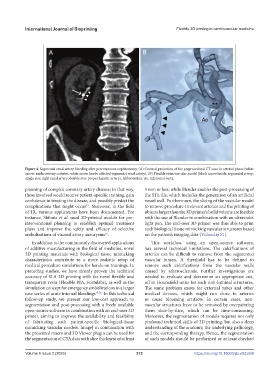
Figure 4. Segmental renal artery bleeding after percutaneous nephrostomy. (A) Coronal projection of the preprocedural CT scan in arterial phase (white
arrow: nephrostomy catheter; white arrow heads: affected segmental renal artery). (B) Flexible resin vascular model (black arrow heads: segmental artery;
single star: right renal artery; double star: proper hepatic artery). Abbreviation: Ao, infrarenal aorta.
planning of complex coronary artery disease; in that way, 1 mm or less, while Blender enables the post-processing of
those involved would receive patient-specific training, gain the STL file, which includes the generation of an artificial
confidence in treating the disease, and possibly predict the vessel wall. Furthermore, the slicing of the vascular model
15
complications that might occur . Moreover, in the field to remove procedure-irrelevant arteries and the printing of
of IR, various applications have been documented. For objects larger than the 3D printer’s build volume are feasible
instance, Shibata et al. used 3D-printed models for pre- with the use of Blender in combination with an ultraviolet
interventional planning to establish optimal treatment light pen. The end-user 3D printer was thus able to print
plans and improve the safety and efficacy of selective such biological tissue mimicking vascular structures based
16
embolizations of visceral artery aneurysms . on the patient’s imaging data (Videoclip S1).
In addition to the continuously discovered applications This workflow, using an open-source software,
of additive manufacturing in the field of medicine, novel has several technical limitations. The calcifications of
3D printing materials with biological tissue mimicking arteries can be difficult to remove from the segmented
characteristics contribute to a more realistic setup of vascular lumen. A threshold has to be defined to
medical procedure simulations for hands-on trainings. In remove such calcifications from the vascular walls
preceding studies, we have already proven the technical caused by atherosclerosis. Further investigations are
accuracy of SLA 3D printing with the novel flexible and needed to evaluate and determine an appropriate cut-
transparent resin (Flexible 80A, Formlabs), as well as the off in Hounsfield units for such non-luminal structures.
simulation concept for emergency embolizations in a larger The same problem exists for external tubes and other
case series of acute internal bleedings 17,18 . In this technical medical devices, which might run close to arteries
follow-up study, we present our low-cost approach to or cause blooming artifacts. In certain cases, non-
segmentation and post-processing with a freely available vascular structures have to be removed by overpainting
open-source software in combination with an end-user 3D them slice-by-slice, which can be time-consuming.
printer, aiming to improve the availability and feasibility Moreover, the segmentation of models requires not only
of fabricating such patient-specific biological-tissue profound technical skills of 3D printing, but also a deep
mimicking vascular models. ImageJ in combination with understanding of the anatomy, the underlying pathology,
the presented macro and 3D Viewer plugin can be used for and the corresponding therapy. Hence, the segmentation
the segmentation of CTA data with slice thickness of at least of such models should be performed or at least checked
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 312 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.669