Page 407 - IJB-9-2
P. 407
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed skin substitute accelerates wound healing in vivo
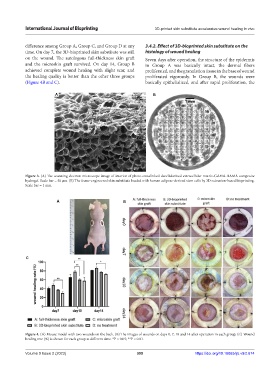
difference among Group A, Group C, and Group D at any 3.4.2. Effect of 3D-bioprinted skin substitute on the
time. On day 7, the 3D-bioprinted skin substitute was still histology of wound healing
on the wound. The autologous full-thickness skin graft Seven days after operation, the structure of the epidermis
and the microskin graft survived. On day 14, Group B in Group A was basically intact, the dermal fibers
achieved complete wound healing with slight scar, and proliferated, and the granulation tissue in the base of wound
the healing quality is better than the other three groups proliferated vigorously. In Group B, the wounds were
(Figure 4B and C). basically epithelialized, and after rapid proliferation, the
A B
Figure 3. (A) The scanning electron microscope image of interior of photo-crosslinked decellularized extracellular matrix-GelMA-HAMA composite
hydrogel. Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) The tissue-engineered skin substitute loaded with human adipose-derived stem cells by 3D extrusion-based bioprinting.
Scale bar = 1 mm.
A B
C
Figure 4. (A) Mouse model with two wounds on the back. (B) The images of wounds on days 0, 7, 10 and 14 after operation in each group. (C) Wound
healing rete (%) is shown for each group at different time. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 399 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.674