Page 75 - IJB-9-3
P. 75
International Journal of Bioprinting 3DP hydrogels to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria
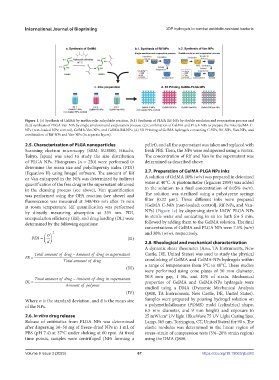
Figure 1. (a) Synthesis of GelMA by methacrylic anhydride reaction. (b.1) Synthesis of PLGA Rif-NPs by double emulsion and evaporation process and
(b.2) synthesis of PLGA Van-NPs by single emulsion and evaporation process. (c) Combination of GelMA and PLGA NPs to prepare the inks: GelMA-C-
NPs (non-loaded NPs; control), GelMA-Van-NPs, and GelMA-Rif-NPs. (d) 3D Printing of GelMA hydrogels containing C-NPs, Rif-NPs, Van-NPs, and
combination of Rif-NPs and Van-NPs (in separate layers).
2.5. Characterization of PLGA nanoparticles pellet), and all the supernatant was taken and replaced with
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM; SU8000, Hitachi, fresh PBS. Then, the NPs were redispersed using a vortex.
Tokyo, Japan) was used to study the size distribution The concentration of Rif and Van in the supernatant was
of PLGA NPs. Histograms (n = 250) were performed to determined as described above.
determine the mean size and polydispersity index (PDI)
(Equation II) using ImageJ software. The amount of Rif 2.7. Preparation of GelMA-PLGA NPs inks
or Van entrapped in the NPs was determined by indirect A solution of GelMA 10% (w/v) was prepared in deionized
quantification of the free drug in the supernatant obtained water at 40°C. A photoinitiator (Irgacure 2959) was added
in the cleaning process (see above), Van quantification to the solution to a final concentration of 0.05% (w/v).
was performed using the OPA reaction (see above) and The solution was sterilized using a polystyrene syringe
fluorescence was measured at 340/455 nm after 15 min filter (0.22 µm). Three different inks were prepared
at room temperature. Rif quantification was performed (GelMA C-NPs [non-loaded; control], Rif-NPs, and Van-
by directly measuring absorption at 335 nm. PDI, NPs) (Figure 1c) by dispersing sterile LMW PLGA NPs
encapsulation efficiency (EE), and drug loading (DL) were in sterile water and sonicating in an ice bath for 5 min,
determined by the following equations: followed by adding them to the GelMA solution. The final
concentrations of GelMA and PLGA NPs were 7.5% (w/v)
2 and 30% (w/w), respectively.
σ
PDI = (II) 2.8. Rheological and mechanical characterization
d
A dynamic shear rheometer (Ares, TA Instruments, New
Totalamountofdrug − Amountofdrugin supernatant Castle, DE, United States) was used to study the physical
EE = crosslinking of GelMA and GelMA-NPs hydrogels within
Totalamountoffdrug
(III) a range of temperatures from 5°C to 40°C. These studies
were performed using cone plates of 50 mm diameter,
50.8 mm gap, 1 Hz, and 10% of strain. Mechanical
Totalamountofdrug − Amountofdrugin supernatant
DL = properties of GelMA and GelMA-NPs hydrogels were
Amount of polymmer studied using a DMA (Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
(IV) Q800, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, United States).
Where σ is the standard deviation, and d is the mean size Samples were prepared by pouring hydrogel solution on
of the NPs. a polymethylsiloxane (PDMS) mold (cylindrical shape,
6.5 mm diameter, and 9 mm height) and exposure to
2.6. In vitro drug release 25 mW/cm UV light (BlueWave 75 UV Light Curing Spot
2
Release of antibiotics from PLGA NPs was determined Lamp, 365 nm, Torrington, CT, United States) for 90 s. The
after dispersing 30–50 mg of freeze-dried NPs in 1 mL of elastic modulus was determined in the linear region of
PBS (pH 7.4) at 37°C under shaking at 60 rpm. At fixed stress–strain of compression tests (5%–20% strain region)
time points, samples were centrifuged (NPs forming a using the DMA Q800.
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 67 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.683