Page 79 - IJB-9-3
P. 79
International Journal of Bioprinting 3DP hydrogels to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Figure 3. Rheological analysis of GelMA and GelMA-C-NPs. (a) Storage and loss modulus and (b) sol-gel temperatures of GelMA and GelMA-C-NPs, and
(c) viscosity of GelMA 7.5 % (w/v) - C-NPs 30 % (w/w).
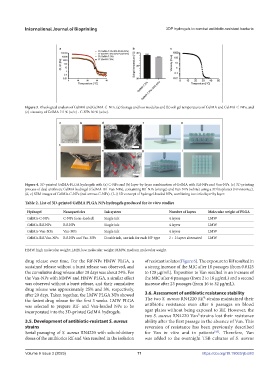
Figure 4. 3D-printed GelMA-PLGA hydrogels with (a) C-NPs and (b) layer-by-layer combination of GelMA with Rif-NPs and Van-NPs. (c) 3D printing
process of dual antibiotic GelMA hydrogel (GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs), containing Rif-NPs (orange) and Van-NPs (white) using a 3D bioplotter (Envisiontec).
(d, e) SEM images of GelMA-C-NPs (red arrows C-NPs). (f–i) 3D concept of hydrogel-loaded NPs, combining two inks layer by layer.
Table 2. List of 3D-printed GelMA PLGA NPs hydrogels produced for in vitro studies
Hydrogel Nanoparticles Ink system Number of layers Molecular weight of PLGA
GelMA-C-NPs C-NPs (non-loaded) Single ink 4 layers LMW
GelMA-Rif-NPs Rif-NPs Single ink 4 layers LMW
GelMA-Van-NPs Van-NPs Single ink 4 layers LMW
GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs Rif-NPs and Van-NPs Double ink, one ink for each NP type 2 + 2 layers alternated LMW
HMW, high molecular weight; LMH, low molecular weight; MMW, medium molecular weight.
drug release over time. For the Rif-NPs HMW PLGA, a of resistant isolates (Figure 6). The exposure to Rif resulted in
sustained release without a burst release was observed, and a strong increase of the MIC after 10 passages (from 0.0125
the cumulative drug release after 20 days was about 24%. For to 128 µg/mL). Exposition to Van resulted in an increase of
the Van-NPs with MMW and HMW PLGA, a similar effect the MIC after 4 passages (from 2 to 16 µg/mL) and a second
was observed without a burst release, and their cumulative increase after 23 passages (from 16 to 32 µg/mL).
drug release was approximately 25% and 3%, respectively,
after 20 days. Taken together, the LMW PLGA NPs showed 3.6. Assessment of antibiotic resistance stability
R
the fastest drug release for the first 3 weeks. LMW PLGA The two S. aureus RN4220 Rif strains maintained their
was selected to prepare Rif- and Van-loaded NPs to be antibiotic resistance even after 6 passages on blood
incorporated into the 3D-printed GelMA hydrogels. agar plates without being exposed to Rif. However, the
two S. aureus RN4220 Van strains lost their resistance
R
3.5. Development of antibiotic-resistant S. aureus ability after the first passage in the absence of Van. This
strains reversion of resistance has been previously described
Serial passaging of S. aureus RN4220 with sub-inhibitory for Van in vitro and in patients [43] . Therefore, Van
doses of the antibiotics Rif and Van resulted in the isolation was added to the overnight TSB cultures of S. aureus
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 71 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.683