Page 82 - IJB-9-3
P. 82
International Journal of Bioprinting 3DP hydrogels to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria
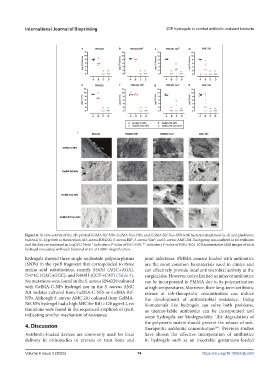
Figure 8. In vitro activity of the 3D-printed GelMA-Rif-NPs, GelMA-Van-NPs, and GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs with bacterial attachment (a–d) and planktonic
bacterial (e–h) growth in the medium of S. aureus RN4220, S. aureus Rif , S. aureus Van , and S. aureus AMC 201. Each group was analyzed in six replicates
R
R
and the data are expressed in LogCFU. Note: * indicates a P-value of 0.01–0.05, ** indicates a P-value of 0.001–0.01. (i) Representative SEM images of each
hydrogel inoculated with each bacterial strain at 1,000× magnification.
hydrogels showed three single nucleotide polymorphisms joint infections. PMMA cement loaded with antibiotics
(SNPs) in the rpoB fragment that corresponded to three are the most common biomaterials used in clinics and
amino acid substitutions, namely S463R (AGC→AGA), can effectively provide local antimicrobial activity at the
D471G (GAC→GGC), and R484H (CGT→CAT) (Table 3). surgical site. However, only a limited number of antibiotics
No mutations were found in the S. aureus RN4220 cultured can be incorporated in PMMA due to its polymerization
with GelMA-C-NPs hydrogel nor in the S. aureus AMC at high temperatures. Moreover, their long-term antibiotic
201 isolates cultured from GelMA-C-NPs or GelMA-Rif- release at sub-therapeutic concentration can induce
NPs. Although S. aureus AMC 201 cultured from GelMA- the development of antimicrobial resistance. Using
Rif-NPs hydrogel had a high MIC for Rif (>128 µg/mL), no biomaterials like hydrogels can solve both problems,
mutations were found in the sequenced amplicon of rpoB, as thermo-labile antibiotics can be incorporated and
indicating another mechanism of resistance. some hydrogels are biodegradable. The degradation of
the polymeric matrix should prevent the release of sub-
4. Discussion therapeutic antibiotic concentration . Previous studies
[44]
Antibiotic-loaded devices are commonly used for local have shown the effective incorporation of antibiotics
delivery in orthopedics to prevent or treat bone and in hydrogels such as an injectable gentamicin-loaded
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 74 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.683