Page 81 - IJB-9-3
P. 81
International Journal of Bioprinting 3DP hydrogels to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria
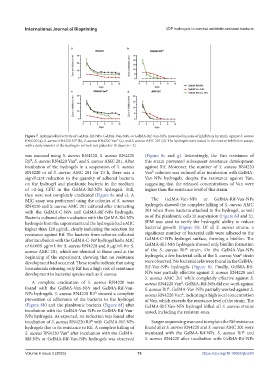
Figure 7. Antimicrobial activity of GelMA-Rif-NPs, GelMA-Van-NPs, or GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs, measured in zone of inhibition (in mm), against S. aureus
R
R
RN4220 (a), S. aureus RN4220 Rif (b), S. aureus RN4220 Van (c), and S. aureus AMC 201 (d). The hydrogels were tested in the zone of inhibition assays,
with a daily transfer of the hydrogels to fresh test plates for 10 days (n = 3).
was assessed using S. aureus RN4220, S. aureus RN4220 (Figure 8c and g). Interestingly, the Van resistance of
Rif , S. aureus RN4220 Van , and S. aureus AMC 201. After this strain prevented subsequent resistance development
R
R
incubation of the hydrogels in a suspension of S. aureus against Rif. Moreover, the number of S. aureus RN4220
RN4220 or of S. aureus AMC 201 for 24 h, there was a Van colonies was reduced after incubation with GelMA-
R
significant reduction in the quantity of adhered bacteria Van-NPs hydrogels, despite the resistance against Van,
on the hydrogel and planktonic bacteria in the medium suggesting that the released concentrations of Van were
of >2-log CFU in the GelMA-Rif-NPs hydrogels. Still, higher than the resistance level of this strain.
they were not completely eradicated (Figure 8a and e). A
MIC assay was performed using the colonies of S. aureus The GelMA-Van-NPs or GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs
RN4220 and S. aureus AMC 201 cultured after interacting hydrogels showed the complete killing of S. aureus AMC
with the GelMA-C-NPs and GelMA-Rif-NPs hydrogels. 201 when these bacteria attached to the hydrogel, as well
Bacteria cultured after incubation with the GelMA-Rif-NPs as of the planktonic cells in suspension (Figure 8d and h).
hydrogels from the supernatant and the hydrogels had a MIC SEM was used to verify the hydrogels’ ability to reduce
higher than 128 µg/mL, clearly indicating the selection for bacterial growth (Figure 8i). Of all S. aureus strains, a
resistance against Rif. The bacteria from colonies collected significant number of bacterial cells were adhered to the
after incubation with the GelMA-C-NP hydrogel had a MIC GelMA-C-NPs hydrogel surface, forming a biofilm. The
of 0.0019 μg/mL for S. aureus RN4220 and 8 µg/mL for S. GelMA-Rif-NPs hydrogels showed only biofilm formation
R
aureus AMC 201, which are identical to those used at the of the S. aureus Rif strain. On the GelMA-Van-NPs
R
beginning of the experiment, showing that no resistance hydrogels, a few bacterial cells of the S. aureus Van strain
development had occurred. These results indicate that using were observed. No bacterial cells were found in the GelMA-
biomaterials releasing only Rif has a high risk of resistance Rif-Van-NPs hydrogels (Figure 8). Finally, GelMA-Rif-
development in bacterial species such as S. aureus. NPs was partially effective against S. aureus RN4220 and
S. aureus AMC 201 while completely effective against S.
A complete eradication of S. aureus RN4220 was aureus RN4220 Van . GelMA-Rif-NPs did not work against
R
found with the GelMA-Van-NPs and GelMA-Rif-Van- S. aureus Rif . GelMA-Van-NPs partially worked against S.
R
NPs hydrogels. S. aureus RN4220 Rif showed a complete aureus RN4220 Van , indicating a high local concentration
R
R
prevention of adherence of the bacteria to the hydrogel of Van, which exceeds the resistance level of the strain. The
(Figure 8b) and the planktonic bacteria (Figure 8f) after GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs hydrogel killed all S. aureus strains
incubation with the GelMA-Van-NPs or GelMA-Rif-Van- tested, including the resistant ones.
NPs hydrogels. As expected, no reduction was found after
incubation of S. aureus RN4220 Rif with GelMA-Rif-NPs Sanger sequencing was used to explain the Rif resistance
R
hydrogels due to its resistance to Rif. A complete killing of found after S. aureus RN4220 and S. aureus AMC 201 were
S. aureus RN4220 Van after incubation with the GelMA- incubated with the GelMA-Rif-NPs. S. aureus Rif and
R
R
Rif-NPs or GelMA-Rif-Van-NPs hydrogels was observed S. aureus RN4220 after incubation with GelMA-Rif-NPs
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 73 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.683