Page 141 - IJB-9-5
P. 141
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed PEEK scaffold mediates macrophages to affect osseointegration
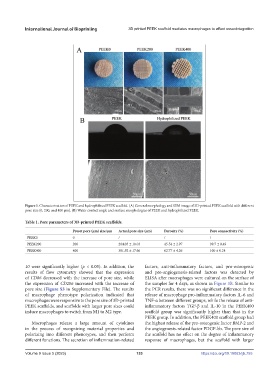
Figure 1. Characterization of PEEK and hydrophilized PEEK scaffold. (A) General morphology and SEM image of 3D-printed PEEK scaffold with different
pore size (0, 200, and 400 μm). (B) Water contact angle and surface morphologies of PEEK and hydrophilized PEEK.
Table 1. Pore parameters of 3D-printed PEEK scaffolds.
Preset pore (μm) size/μm Actual pore size (μm) Porosity (%) Pore connectivity (%)
PEEK0 0 / / /
PEEK200 200 204.03 ± 10.03 45.54 ± 2.97 99.7 ± 0.49
PEEK400 400 381.92 ± 17.66 62.77 ± 4.26 100 ± 0.24
10 were significantly higher (p < 0.05). In addition, the factors, anti-inflammatory factors, and pro-osteogenic
results of flow cytometry showed that the expression and pro-angiogenesis-related factors was detected by
of CD86 decreased with the increase of pore size, while ELISA after macrophages were cultured on the surface of
the expression of CD206 increased with the increase of the samples for 4 days, as shown in Figure 3B. Similar to
pore size (Figure S3 in Supplementary File). The results the PCR results, there was no significant difference in the
of macrophage phenotype polarization indicated that release of macrophage pro-inflammatory factors IL-6 and
macrophages were responsive to the pore size of 3D-printed TNF-α between different groups, while the release of anti-
PEEK scaffolds, and scaffolds with larger pore sizes could inflammatory factors TGF-β and IL-10 in the PEEK400
induce macrophages to switch from M1 to M2 type. scaffold group was significantly higher than that in the
PEEK group. In addition, the PEEK400 scaffold group had
Macrophages release a large amount of cytokines the highest release of the pro-osteogenic factor BMP-2 and
in the process of recognizing material properties and the angiogenesis-related factor PDGF-bb. The pore size of
polarizing into different phenotypes, and then perform the scaffold has no effect on the degree of inflammatory
different functions. The secretion of inflammation-related response of macrophages, but the scaffold with larger
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 133 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.755