Page 457 - IJB-9-5
P. 457
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed oblique lumbar interbody cage
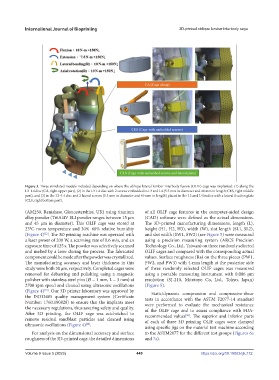
Figure 3. Three simulated models included depending on where the oblique lateral lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) cage was implanted: (1) along the
L3–L4 disc (CA, right upper part), (2) in the L3-L4 disc with 2 screws embedded in L3 and L4 (5.5 mm in diameter and 40 mm in length; CES, right middle
part), and (3) in the L3–L4 disc and 2 lateral screws (5.5 mm in diameter and 40 mm in length) placed in the L3 and L4 bodies with a lateral fixation plate
(CLS, right bottom part).
(AM250, Renishaw, Gloucestershire, UK) using titanium of all OLIF cage features in the computer-aided design
alloy powder (Ti6Al4V ELI powder ranges between 15 μm (CAD) software were defined as the actual dimensions.
and 45 μm in diameter). This OLIF cage was stored at The 3D-printed manufacturing dimensions, length (L),
23°C room temperature and 30%–60% relative humidity height (H1, H2, H3), width (W), slot length (SL1, SL2),
[22]
(Figure 4) . The 3D printing machine was operated with and slot width (SW1, SW2) (see Figure 5) were measured
a laser power of 200 W, a scanning rate of 0.6 m/s, and an using a precision measuring system (ARCS Precision
exposure time of 125 s. The powder was selectively scanned Technology Co., Ltd., Taiwan) on three randomly selected
and melted by a laser during the process. The fabricated OLIF cages and compared with the corresponding actual
component could be made after the powder was crystallized. values. Surface roughness (Ra) on the three pieces (PW1,
The manufacturing accuracy and layer thickness in this PW2, and PW3) with 4-mm length at the posterior side
study were both 30 μm, respectively. Completed cages were of three randomly selected OLIF cages was measured
removed for deburring and polishing using a magnetic using a portable measuring instrument with 0.006 µm
polisher with stainless steel pins (Ø = 1 mm, L = 3 mm) at resolution (SJ-210, Mitutoyo Co, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan)
2700 rpm speed and cleaned using ultrasonic oscillations (Figure 5).
[24]
(Figure 4) . Our 3D printer laboratory was approved by Static/dynamic compression and compressive-shear
the ISO13485 quality management system (Certificate tests in accordance with the ASTM F2077-14 standard
Number: 1760.190828) to ensure that the implants meet were performed to evaluate the mechanical resistance
the necessary regulations, thus assuring safety and quality. of the OLIF cage and to assess compliance with FDA-
After 3D printing, the OLIF cage was acid-etched to recommended values . The superior and inferior parts
[26]
remove residual sandblast particles and cleaned using of each of three 3D printing OLIF cages were clamped
[24]
ultrasonic oscillations (Figure 4) . using specific jigs on the material test machine according
For analysis on the dimensional accuracy and surface to the ASTM2077 for the different test groups (Figures 6a
roughness of the 3D-printed cage, the detailed dimensions and 7a).
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 449 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.772