Page 477 - IJB-9-6
P. 477
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting cell-laden protein-based hydrogel
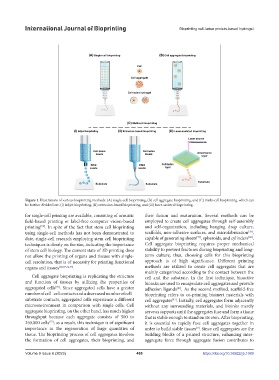
Figure 1. Illustrations of various bioprinting methods: (A) single-cell bioprinting, (B) cell aggregate bioprinting, and (C) multi-cell bioprinting, which can
be further divided into (i) inkjet bioprinting, (ii) extrusion-based bioprinting, and (iii) laser-assisted bioprinting.
for single-cell printing are available, consisting of acoustic their fusion and maturation. Several methods can be
field-based printing or label-free computer vision-based employed to create cell aggregates through self-assembly
printing . In spite of the fact that stem cell bioprinting and self-organization, including hanging drop culture,
[73]
[78]
using single-cell methods has not been demonstrated to scaffolds, non-adhesive surfaces, and microfabrication ,
[79]
[80]
date, single-cell research employing stem cell bioprinting capable of generating sheets , spheroids, and cylinders .
techniques is clearly on the rise, indicating the importance Cell aggregate bioprinting requires proper mechanical
of stem cell biology. The current state of 3D printing does stability to prevent fractures during bioprinting and long-
not allow the printing of organs and tissues with single- term culture; thus, choosing cells for this bioprinting
cell resolution, that is of necessity for printing functional approach is of high significance. Different printing
organs and tissues [68,69,74,75] . methods are utilized to create cell aggregates that are
mainly categorized according to the contact between the
Cell aggregate bioprinting is replicating the structure cell and the substrate. In the first technique, bioactive
and function of tissues by utilizing the properties of bioinks are used to encapsulate cell aggregates and provide
aggregated cells . Since aggregated cells have a greater adhesion ligands . As the second method, scaffold-free
[76]
[81]
number of cell–cell contacts and a decreased number of cell– bioprinting refers to co-printing bioinert materials with
substrate contacts, aggregated cells experience a different cell aggregates . Initially, cell aggregates form adjacently
[82]
microenvironment in comparison with single cells. Cell without any surrounding materials, and bioinks merely
aggregate bioprinting, on the other hand, has much higher serve as supports until the aggregates fuse and form a tissue
throughput because each aggregate consists of 500 to that is stable enough to stand on its own. After bioprinting,
250,000 cells ; as a result, this technique is of significant it is essential to rapidly fuse cell aggregates together in
[77]
importance in the regeneration of large quantities of order to build stable tissues . Since cell aggregates are the
[9]
tissue. The bioprinting process of cell aggregates involves building blocks of a printed structure, enhancing inter-
the formation of cell aggregates, their bioprinting, and aggregate force through aggregate fusion contributes to
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 469 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1089